In the cable industry, you may find many options for wiring your commercial or residential buildings. However, selecting the right cable will save you from future losses of cable degradation over time.
Thus, selecting the right cable type, considering the color and size factors is a crucial factor during the wiring of your building.
THHN wire is one of the most common choices of your electrician today. It exhibits several advantages that help you from future loss and provides a long-term solution for your building wiring system.
However, it’s important to remember that THHN wire is not suitable for direct burial. So, you need to consult any subject matter expert or electrician for the proper installation following local building codes.
Thus, in this business blog, we will see some of the important features of THHN wire specifications and how it is different from other building wires like Romex® and XHHW.
What does thhn wire mean?

When people buy thn wire they always ask about “what does thhn stand for in wire”. THHN wire refers, to “Thermoplastic High Heat-Resistant, Nylon-Coated”, while THWN, refers to “Thermoplastic High Water-Resistant, Nylon-Coated.”
THHN wire is commonly used in building wiring systems. It’s the insulated wire with single-core conductors insulated or surrounded by PVC insulation and a nylon jacket.
Thhn wire is famous for its heat resistance, moisture resistance, and durability, which makes it applicable for various indoor and outdoor electrical appliances, especially in wet environments.
Thhn wire’s copper conductor can be solid or stranded. The insulation is PVC, and the sheath is nylon. Thhn-2 is essentially the same as thhn.
After a brief understanding of the thnn wire, let’s take a deeper study of thhn stranded wire specification.
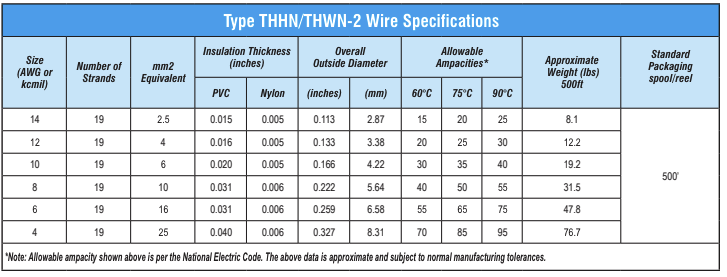
THHN/THWN-2 Cables Specification
THHN/THWN-2 is the type of building wire. Its code standard is defined by the National Electrical Code (NEC). This cable is used primarily for the rewiring of 600 volts or new construction. Let’s find out some of the important features of THHN/THWN-2 cables below:
Specifications
- Conductors: The conductor materials of THHN/THWN-2 cable are stranded, uncoated copper or aluminum. The copper type includes the standard types ASTM-B8, ASTM-B3, and ASTM-B787.
- Insulation: It uses the thermoplastic insulator-type Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC Cable), flame retardant. It is heat- and moisture-resistant.
- Jacket: It consists of the Bylon jacket, providing an outer covering. It has the standards UL-83 and UL-1063.
- Temperature Rating: The temperature rating of THHN cables in dry or wet areas is around 90 degrees while in oil and coolants the selected temperature is around 75 degrees.
Additional Features
- The insulation can withstand sunlight exposure without degrading.
- This cable has the next interesting properties of oil and coolant resistance. It helps to make it a suitable choice in an industrial environment.
Difference between Romex with Thhn Wire
If you check out the Romex® and THHN cables, then you will see, that both of them are widely used in electrical wiring systems. However, you can find some differences in their construction and applications. So, let’s find out how they differ regarding applications, construction, and more.
Construction
- If you check inside Romex® wire, it consists of two or more conductors. Each of these conductors is insulated individually. Then the whole bundle is surrounded by an outer jacket. So, romex® wires are like bundles of THHN wires wrapped in PVC.
- Whereas, THHN wire is a type of single-conductor wire surrounded by a nylon jacket.
Application
- Romex® is widely used for indoor applications due to its less durable PVC jacket which makes it a cheaper option as compared to THHN wire.
- THHN is more versatile than Romex®. You can use it for both indoor and outdoor applications based on your application requirements.
Code Compliance
- The building code restricts the use of Romex® in residential buildings.
- THHN wire is approved by building codes. Thus, you can use them for the wiring system of commercial or residential buildings.
THHN vs. XHHW-2: What’s the Difference

THHN/THWN-2 has a thermoplastic insulation, while XHHW-2 is a thermoset insulation. Thermoplastic is cheaper than thermoset and nylon coating is required for the insulation system’s rating. THHN and XHHW-2 differ in many factors. Some of the common points are explained below:
Insulation
- The insulation of THHN wire is polyvinyl chloride with a nylon jacket.
- While XHHW-2 is insulated with Cross-Linked Polyethylene (XLPE). The insulation is heat and water-resistant.
Flexibility
- The thermoplastic insulation of THHN makes it less flexible than XHHW-2.
- Whereas, the XLPE insulation in XHHW-2 enhances flexibility and makes the process easier, especially in tight spaces.
Jacket
- THHN has a thinner nylon jacket. It allows more THHN wires to fit in tight spaces.
- XHHW-2 has a thicker and more robust jacket. It helps provide better protection against physical damage.
Cost
- THHN is less expensive and is cost-effective, because of the use of simple materials.
- The use of XLPE insulation makes the XHHW-2 more expensive than THHN for wiring applications.
Applications
- You can use, THHN in residential and commercial applications where there is minimal moisture exposure.
- While you can use XHHW-2 in industrial and outdoor applications. The usage of XHHW-2 is common in high temperatures and chemically exposed environments.
Below is the table for a quick comparison:
| Feature | THHN | XHHW-2 |
| Insulation | PVC | Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE) |
| Temperature Rating (Dry/Wet) | 90°C (dry/wet) / 75°C(oil/coolant) | 90°C / 90°C(for all conditions) |
| Flexibility | Less flexible due to PVC insulations | More flexible due to XLPE insulations |
| Cost | Less expensive | More expensive |
| Applications | General- purpose, commercial or residential buildings | Used in demanding environments, with high temperatures, moisture, etc. |
Also Learn: THHN VS XHHW: Characteristics, Differences And Consideration
Thhn wire Conclusion
You need to select the right cable for your building wire for long-term reliability. THHN wire stands out for its heat and moisture resistance. This makes it a suitable choice for indoor and outdoor applications.
However, you need to follow the local building codes during installation.
THHN wires offer versatility, while XHHW-2 helps in challenging environments. Also consider, that THHN wire is best for dry locations.
So, this way, we check out the differences between various types of building wires and their applications in various environmental conditions.
If you are searching for the right thhn wire manufacturers, then look no further than ZW Cables. With about 30 years of service, ZW Cables is a modernized and large-scale thhn cu wire producer all over China today. We follow all the required standards and have passed all the certifications needed for thhn wire.
So, contact us today and request a quote. We will guide you through the right selection of thhn wire for your applications.
Thnn wire FAQS
Can THHN wire be buried?
Thhn cable can be buried. However, burying the wires requires consideration of certain aspects, such as burial depth, conduit, the way the wiring is underground, and grounding.
Different regions have regulations and requirements; the burial depth is usually 457.2mm, but the specific depth still has to follow the local regulations. In order to minimize the damage, THHN and THWN-2 should be buried in conduit. During the wiring, be careful to pull the rope. Because it can sometimes damage the insulation. Grounding needs to be installed in specific locations and you need to safely do it.
What is the difference between AWG and the wire?
Americal Wire Gauge (AWG) is the measurement system that indicates the dimensions of wire and it is also used to measure the thickness of THHN wire.
THHN wire specifies the wire types with the insulation of thermoplastic material, often used for dry and moist locations for electrical cables. THHN wire is common in commercial and residential environments.