Choosing between single-core or multi-core cables has long been a topic of interest and debate among cabling, and the choice between the two can significantly impact the efficiency, safety, and functionality of electrical installations. Therefore, understanding single-core vs multi-core cable is crucial for making informed decisions. We will delve into the difference between single-core and multicore cables, comparing their characteristics and applications, and providing considerations when choosing between them. Let’s begin.
What is single core cable?
Single core cable, as the name implies, is a type of cable that contains a single conductor, typically made of copper or aluminum. Single-core cable is engineered to facilitate a single path for transmitting electricity, are highly voltage resistant, and is the most commonly used cables for large-scale power transmission. Due to the high flexibility afforded by its simple construction, single-core cables are apt for a variety of applications ranging from residential wiring to industrial power distribution systems. The solid or strand copper conductor within single core wire is encased in protective insulation (usually PVC or XLPE), providing corrosion resistance and durability. Common single core cable sizes are 1.5 mm single core cable and 4mm single core cable.

Having established what single core electrical cables are, we now turn to single core cable types.
Types of single core cable.
Single-core cables adopt different materials and are of different types, each customized for specific applications and environments. The most common single core cable types are PVC insulated single cable, XLPE insulated cable, rubber insulated cable, and silicone insulated single core cable:
- PVC Insulated Single Core Cable: PVC insulation offers good thermal performance and cost-effectiveness, making PVC-insulated single core cables widely used in home wiring and electrical appliances, with BV, BVR, and RV cables being common.
- XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) Insulated Single Core Cable: Known for their high-temperature resistance and excellent electrical properties, these cables are suitable for power transmission in both underground and overhead systems.
- Rubber Insulated Single Core Cables: Durable and resistant to a wide range of environmental factors, rubber insulated single core cables are often used in flexible applications, such as machinery, tools, and appliances.
- Silicone Insulated Single Core Cable: Typically used in high-temperature environments due to their excellent heat resistance. Common applications include lighting fixtures, industrial machines, and heating appliances.
Whether it’s the cost-effectiveness of PVC, the temperature resistance of XLPE, the durability of rubber, or the heat resistance of silicone, each insulation material endows single-core cables with specific uses. Choosing the right single-core cable type not only meets the requirements of the electrical system, but also ensures safety, efficiency, and service life.
With single-core cables out of the way, let’s take a look at the other another significant category, namely multi-core cables.
What is Multi Core Cable?
Multicore cables consist of multiple conductors bundled within a single cable sheath. The cores can be individually insulated and are capable of carrying multiple signals simultaneously. Multi-core cables are often preferred in complex systems where space is limited and multiple circuits need to operate in parallel with each other. Common applications include low-voltage control systems, communications, data transmission, and powering electrical equipment in buildings. Multi-core cables can be further classified into different types such as twisted pair, control cable, braided cable, and YJV cable for different application scenarios. The high number of conductors in multi-core cables can easily lead to electromagnetic interference with each other, but the use of appropriate shielding materials can effectively reduce such interference.

After recognizing single-core and multi-core cables separately, a comparison of them is in order.
Multi Core vs Single Core Cable.
The main difference between multi-core and single-core cables lies in their construction composition;single-core cables consist of a solitary conductor, whereas multi-core cables are available in configurations such as two-core, three-core, four-core, or higher. The structural difference directly influences their respective applications:
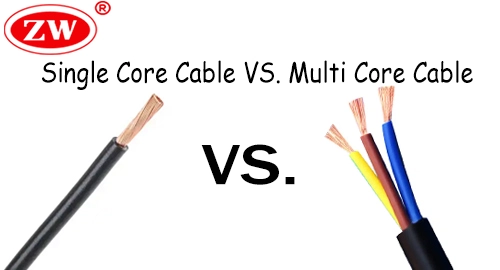
- Single-core cables of the same cross-section can withstand higher currents.
- Multicore cables can experience crosstalk or interference between cores, which is not an issue with single core cables.
- Single core cables typically dissipate heat more effectively, making them suitable for high-current applications.
- Multi core cables are less susceptible to mechanical stress than single-core cables.
- Single-core cables are more convenient for line splicing.
- Multi-core wires are flexible and suitable for moving or bending lines, while single-core wires are more rigid and easier to fix.
- Single-core cables normally have larger diameters than multi-core cables, because the multiple conductors limit the cable to some extent.
- Single-core cables are generally less prone to short circuits and electrical damage as their simple construction reduces the possibility of failure caused by contact within the conductors.
- Under the same burden, single-core cables produce less heat than multi-core cables, rendering them safer to use.
- Multi-core cables consist of multiple conductors, making the manufacturing process more complex and correspondingly more costly.
In summary, single-core cables are preferred for high-current power transmission and environments requiring less flexibility like building wiring and high-voltage substations. In contrast, multi-core cables are more adaptable and better suited for applications with limited space and frequent movement, such as industrial machinery control, automobile wiring, and audio equipment, but are also more costly and more prone to crosstalk. Following these comparisons, we shall now examine the factors that warrant consideration before making a purchase.
When purchasing cables select the appropriate cable based on both.
When purchasing single-core or multi-core cables, a comprehensive selection should be made based on the specific needs of the application, the length required and the budget:
Cable Purpose: For conduit wiring or circuits with voltages of 35kv or above, single-core wires are generally recommended.
Installation Space: Limited space generally uses multi-core cables as they are flexible, less prone to core breakage, and capable of transmitting multiple signals.
Cable Quality: Always invest in high-quality cables as they are durable, trouble-saving, and safe, and it is best to choose certified brand products.
Cable Length: We suggest purchasing the exact cable length based on actual measurements. A cable that is too long will increase the resistance of the cable itself, resulting in increased power loss, while a cable that is too short may not be able to transmit enough power to the target device.
Budget: Single-core cables can be more cost-effective for simple installations.
Appreciating the above factors ensures an informed decision when choosing whether to use a single conductor or a multi-conductor conductor, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness. In the end, let’s draw together all the points discussed.
Conclusion.
To summarize, both single-core and multicore cables have their unique strengths and applications. Understanding the specific requirements of the installation is key to choosing the appropriate cable. As cable quality significantly influences its longevity and safety, opting for a reputable cable manufacturer like ZW Cables to ensure reliability and performance is a wise approach. For accurate single core cable prices, please contact ZW Cable. Below are some frequently asked questions about 1 core cable.
FAQ:
What is Single Core Cable Used For?
Single-core cables are predominantly utilized for power transmission in fixed installations like residential and commercial buildings, as well as in distribution networks, where high current carrying capacity is essential. Due to its high insulation performance, high voltage resistance, and good corrosion resistance, single-core cables are also favored in outdoor applications. They can be found in household appliances, power plugs, transformer wiring, oil refining, chemical and metallurgical industries. Single-core shielded cables are also popular in applications where there is a risk of electromagnetic interference.
Single Core Cable Advantages and Disadvantages.
Single-core cables offer high insulation performance, low electromagnetic interference, and are suitable for high-voltage transmission and outdoor operations. However, they cannot transmit multiple signals, and are vulnerable to mechanical stress. Single core armoured cable cannot be armored with steel wire, but only with non-magnetic metal armor like stainless steel belt or aluminum wire (AWA); because when a single-core cable conducts alternating current, it creates a circular magnetic field around the cable, and the steel armor will create a closed loop, generating eddy currents and causing the cable to heat up.
Single Core Cable Installation Guide.
When installing single-core electrical wire, a thorough site assessment must first be carried out to evaluate environmental and potential mechanical stresses and select the appropriate cable for the rated voltage and capacity. Handle and transport the cable with care, ensuring no twists or kinks, and plan the route according to the bending radius (usually not less than 12 times the cable diameter), using methods like conduits or direct burial as per local regulations. When terminating, carefully strip cables, fit lugs and connectors with correct crimping techniques and ensure secure connections to equipment with waterproof protection. Once the installation is complete, perform electrical tests such as insulation resistance and continuity checks, complemented by visual inspections to verify the installation’s integrity. Finally, comprehensive documentation is kept, and cables are labeled at both ends for future reference and maintenance.
For complex installations, it’s recommended to consult specialized cable manufacturers like ZW Cable.