It is noisy in factories where there is continuous activity and much electricity. It could impede the transparent transmission of signals through the many cables that run communication and control systems.
While insulation helps the cable from things that can score and scrape it and protect it against environmental elements like water and liquid, it does not protect it from electromagnetic interference (EMI). The EMI can get through the insulation and remain in the cables’ signals.
It is what shielding is used for fighting EMI, and ensuring undistorted signals is necessary. It will help if you shield the equipment in electrically noisy areas, like factories.
Do you know?
The average cost for shielded cables is approximately 20% to 30% higher than the non-shielded version due to the extra materials requirements and manufacturing procedures.
What you will learn in this post:
Our business blog will explore the basics of shielded cable and its types and differences.
What is Shielded Cable?

A shielded cable ,or screened cable is an electrical cable engineered to allow signals to travel unhindered while reducing the extent of incidents where signals are invaded by external sources and those trapped inside the cables themselves.
It comprises one or more wires with isolating materials (insulators) and a surrounding conducting layer, which always consists of aluminum or copper. This corrosion-inhibitive layer is called the shield.
The shield has a dual purpose; it does an excellent job of blocking the interference of external electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio frequency interference (RFI) from hampering the signaling ability of the conductors inside the cable. The interferences can be from area communication devices, power cables close by, or radio waves.
In the absence of the shielding, these outward forces may disorient the changing signals, impeding the correct running of the devices.
Shielded wire, for their part, find their use in areas where signal integrity is of paramount importance.
Cases of such applications include data transmission, communications, audio and video equipment, and industrial control systems. They maintain the integrity and fidelity of signals over extended transmission and in poor conditions.
What are the Shielded Cable Types?
The shielded cables cover several varieties, with each array aimed at giving particular protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). Braided cables are crucial in maintaining signal integrity and preventing electronic systems and communication network leakage.
Here are the main types of shielded cables:
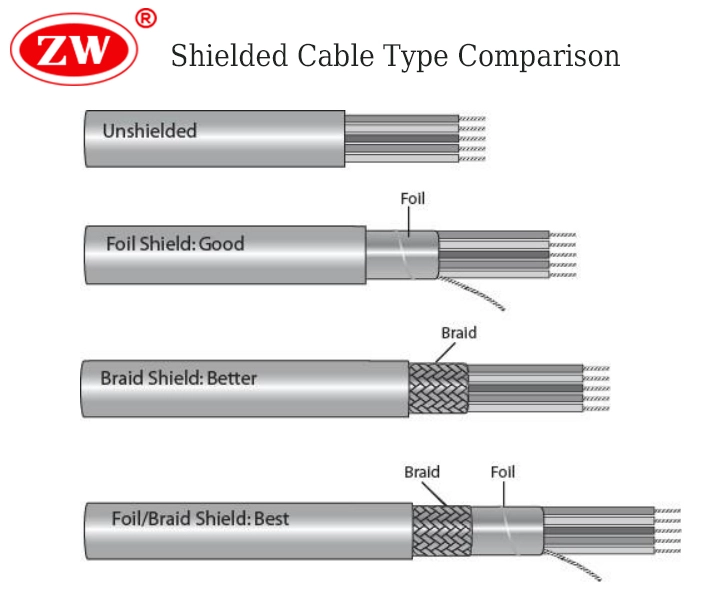
Foiled Shields
Unlike the regular cable, it has a combined braided and foil shield for maintaining greater resistance to interference frequencies. A cable with a foil that can shield high-frequency interference and a braided shield to the cable as an additional barrier against lower-frequency.
Braided Shield
The shield of braid is a net-like or weave of fine metallic wires (copper, tinned copper, or copper-clad aluminum). This mesh is rolling tightly over the insulators.
Also Learn: Tinned Copper Vs Bare Copper: Which One Is Better?
The shield braiding flexibility is undeniably superior to the foil-shielding one, and the former, most certainly, shields more effectively against lower frequencies in comparison to it.
Foiled/Braid Shield Wire
The braid and foil appear simultaneously in this type of cable aimed at blocking interferences at a broader range of frequencies. The foil shield provides (coverage from) high-frequency interference; the braid shield offers (a shield against) low-frequency interference and provides mechanical strength (to this cable).
Cable type selection by engineers is one way to prevent deterioration of the signals. There are many other options, such as screen cable, EMC shielded cable, metal shielded wire, tape shields, combination shields, and twisted cable.
What Is the Purpose Of Shielded In Wire?
The protective sheath of the wire allows the cable to become less susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Here’s a breakdown of how shielding works:
- Blocking external interference:EMI from external sources like power lines, motors, or radio waves can mess with the signal in the wire. The shield acts as a barrier, reflecting or absorbing this EMI and preventing it from reaching the inner conductor.
- Containing internal interference:The shield can also keep the signal within the cable from radiating out, boosting the chances of interfering with other devices. For this purpose, it is essential to abide by the principle of keeping electrical devices in electromagnetic compatibility.
It is something like creating a protective fence encasing the wires. This helps keep the signal contained while preventing external noise from entering.
Shielded cable wires are commonly used in applications where maintaining signal integrity is crucial, such as:
- Computer networks
- Audio/video equipment
- Medical devices
- Instrumentation and control systems
- The automotive industry has shielded automotive wire
Shielded Cable vs. Unshielded
Here are the following differences between shielded and unshielded cables.
1. Shielding
- Shielded Cable:These include another foil wrapping or braided cable of metal mesh wound around the covered lines. This behaves like a coating coaxing noise and interference out of the signal.
- Unshielded Cable:They are not insulated with the more protective layer. They rely solely on twisting the wires within the cable to minimize interference.
2. Signal Integrity
- Shielded Cable:These cables provide shielding, which reduces the amount of signal degradation and most often helps to improve clearness and clarity, particularly at a distance and when there is heavy electrical noise (close to the power line). Moreover, accuracy is much more critical where high data accuracy is required.
- Unshielded Cable: Unprotected cables have a higher chance of spectrum interference, which can reproduce the error or signal strength weakness, especially after running miles in noisy places.
3. Twisting
- Both Shielded and Unshielded Electrical Wire:The two use the same elements and twisted pairs of wires. Twisting the wires helps eliminate a class of interference called crosstalk. The case of crosstalk involves a pair of signal wires; one from the nearby position begins to interfere with the signals from the other pair of cables.
4. Flexibility and Installation
- Shielded Cable:A higher quality shielding increases the stiffness and dimensions of such cables. Those are significantly bigger in bulk than unshielded ones. This adds a little challenge to bending them for installation in relatively narrow spaces.
- Unshielded Cable: Non-shielded cables are easier to route as their complexity is relatively low. This quality enables these machines to operate well when there is the need to perform tight bends or have a lot of movement.
5. Cost
- Shielded Power Cable:The shielding and cable-making connected with manufacturing increase the cost prominently. However, the shielded cable symbol is more expensive than the unshielded one.
- Unshielded Cable: Cost considerations are also a part of the reasons for choosing unshielded wire as they are simpler in design for budgeted installations.
Do you know?
Constant data transfer rates emphasized the cabling feature more in industry publications such as Electronic Design, as the ability to provide better shielding became a must.
These results show that the keeping pace of these shielded cable 4 core and cat6 outdoor cable with the times show that they have maintained their importance throughout technological advancements.
Conclusion
Cables with shielding play a key role in current electronics, ensuring EMI protection and signal control in numerous application fields. This guide helps you to make the right decisions on purchasing and using shielded cables, keeping in mind special conditions and the smooth working of your electronic gadgets and communications.
Reach out to ZW Cable now because we are guaranteed to give you the best shielded ethernet cable and twinax cable etc., to meet your needs.
Our specialized professionals stand to supervise you in choosing the most suitable product for your application. Signals can go down at any time. Please beware of such conditions, talk to us immediately, and have your experience changed!
FAQs:
1. Do Shielded Cables Need To Be Grounded?
As for grounding, an overwhelming majority of grounding shielded cable is required. This leads to interference from any outside source, which is eliminated by the shielding of these cables, although the signal inside the cable may be affected by the same.
2. What Is A Drain Wire In Shielded Cable?
The drain wire is a thin, uninsulated wire already contained in a shielded cable wire. It is an anti-feedback circuit to absorb any stray electrical currents and interference that could leach through the shielding. The drain wire serves as a way to channel this undesirable electrical effect to keep unwanted currents from going to signal-carrying conductors.The cross-sectional area of the drain wire will be smaller than main wire. For example 4 core 2.5mm2 twisted pair shielded cable, the drain wire is 1.5mm2 or 1.0mm2.