Within the expansive realm of electrical engineering, overhead cables, also known as aerial cables, stand as a critical element, facilitating the uninterrupted transmission of electrical energy across extensive distances. These types of overhead cables perform a paramount function in conveying electricity from power production sites to both residential and commercial establishments. This ensures that our global community remains vibrant and interconnected, highlighting the vital role of overhead power cables in maintaining the rhythm of the modern world. In our business blog, We are going to thoroughly investigate the intricacy of overhead wire, as well as its nature, composition, support system, operation of overhead tricep extension mechanism, and safety concerns.
What is overhead cable?
Overhead electrical cables are a type of cable system that is installed above the ground, suspended between poles or towers. These cables are essential components in electrical transmission and distribution systems, carrying electric power from generating stations to individual consumers. In telecommunications, overhead wires facilitate the transmission of data and voice signals across long distances. The installation of overhead service wires, such as low voltage aerial bundled cables, at an elevated position presents multiple professional advantages.
Firstly, it leads to a significant reduction in land utilization, as these cables do not require the extensive excavation associated with underground systems. Secondly, the risk of damage from ground-level hazards, such as flooding or ground shifts, is markedly lower, enhancing the system’s reliability and durability. Lastly, the accessibility of these overhead systems simplifies maintenance procedures, allowing for more efficient and less labor-intensive upkeep compared to their underground counterparts. Let’s focus on materials made from aerial cables.

What are overhead cables made of?
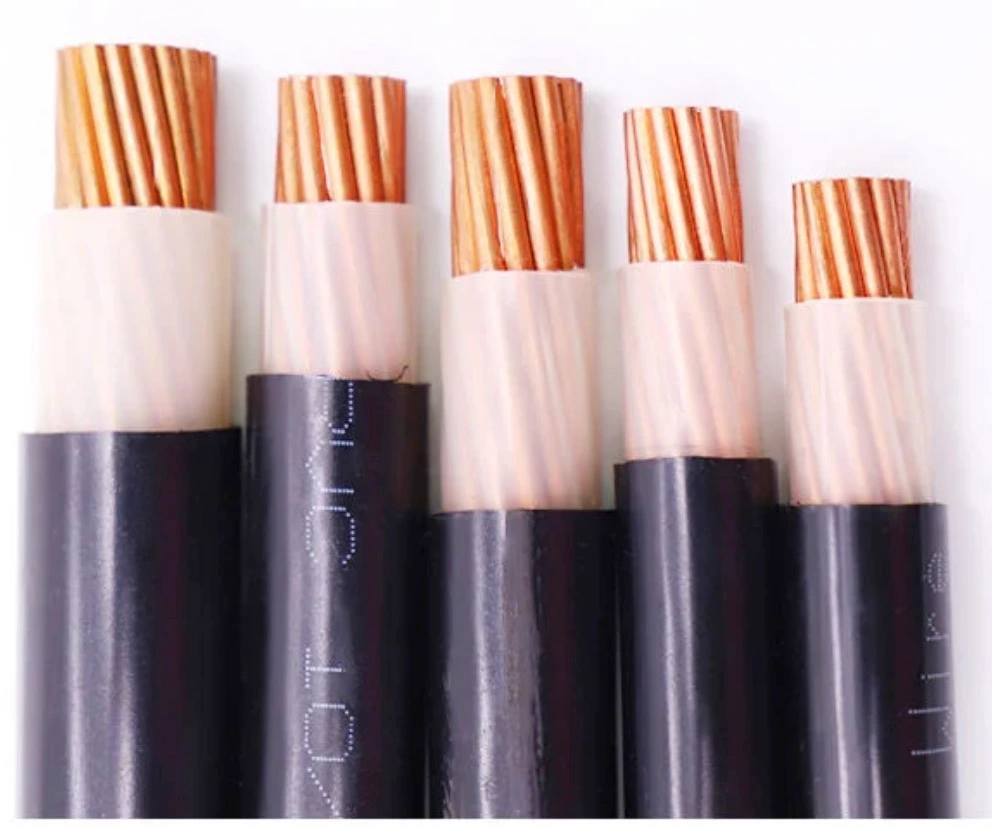
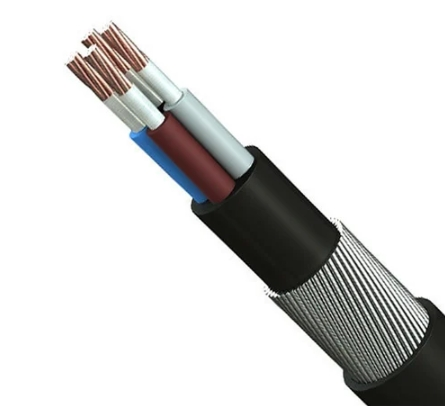
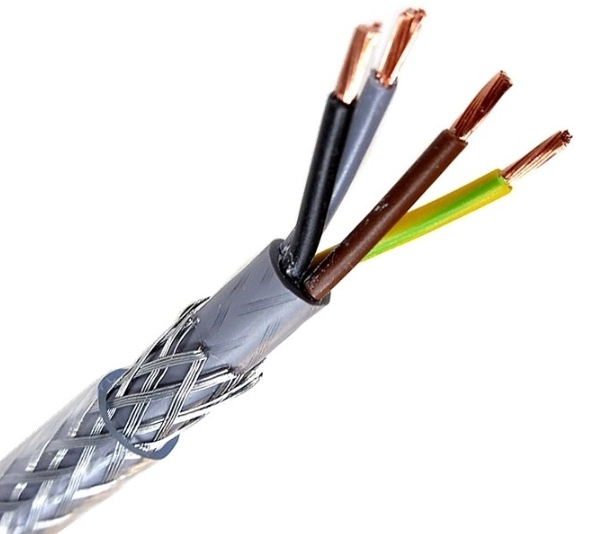
Overhead wire,including service drop wires , are carefully selected usually consisting of aluminum for durability, electrical conductivity and environmental resistance. Electrical power cables typically consist of conductors, insulation, and a protective outer sheath. Overhead aluminum wire being lighter and more cost-effective, is favored for long-distance overhead transmission lines.
Insulation is paramount for maintaining safety and operational efficiency. Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly referred to as XLPE, stands out as a frequently utilized material in this domain. Notably, XLPE cables are highly regarded for their exceptional electrical and thermal resistance, making them particularly beneficial for an array of overhead applications.
These materials are encased in insulating and protective layers, which are crucial for withstanding environmental challenges such as UV radiation, temperature variations, and physical stresses caused by wind or ice. The selection and combination of these materials represent a precise balance between engineering and economics, ensuring that overhead cables not only perform their intended function effectively but also meet the stringent standards of safety and reliability demanded by contemporary technology and infrastructure needs while emphasizing the importance of specialized knowledge and experience in the design and implementation of overhead cable systems. We can then analyze in depth how overhead power lines are supported.

How to support overhead cable?
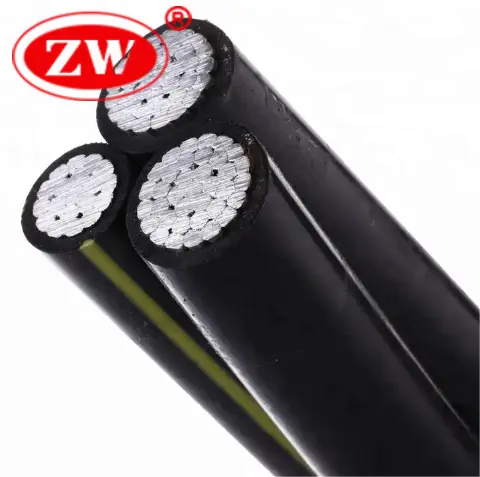
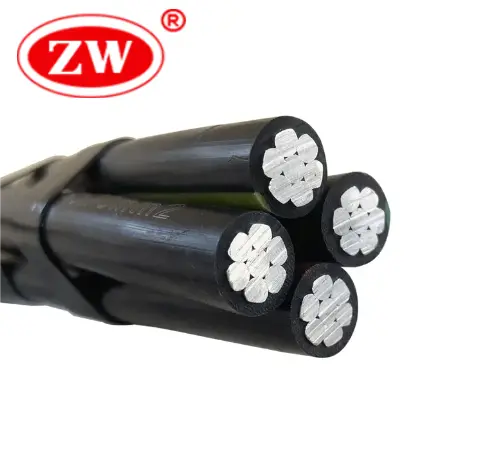
Supporting overhead cables involves a series of steps that ensure both safety and functionality. The process involves several key steps:
Selection of Cable and Structure: it’s important to select the right type of cable for the specific application, considering factors such as the electrical load, environmental conditions, and the distance the cable needs to span.
Installation of Support Structures: Support structures include poles, towers or pylons, which should be placed at strategic intervals to prevent excessive cable sagging, taking into account factors such as wind loads and ice buildup.
Laying and Securing Cables: The cables are then strung and secured, maintaining an optimal balance between tension and flexibility.
Safety Compliance: The installation process should follow industry standards and regulations to ensure safety and durability. This includes using proper insulators and hardware that can withstand environmental stresses while maintaining the integrity of the electrical connection.
Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial for the longevity and safety of the overhead conductor system.
In summary, supporting overhead cable lines requires careful planning, selection of the right materials and structures, adherence to safety standards, and ongoing maintenance to ensure a reliable and safe electrical distribution system.
What does overhead tricep extension work?
In the realm of electrical engineering, it signifies the extension or expansion of overhead service wire systems, such as the triplex overhead wire, for enhanced power distribution capabilities. This design offers a compact, efficient solution for transferring electricity across various distances. The triplex overhead wire, a type of aerial cable, typically consists of three conductors bundled together, designed to efficiently transmit electrical power.
An overhead cable tricep extension, in this case, involves the expansion or elongation of these aerial cables to reach new areas or enhance existing power distribution networks. This process, often termed overhead extension, is crucial for accommodating growing electricity demands or for rerouting power lines due to infrastructural developments. These wires, usually composed of copper or aluminum, are crucial for various functions:
Three-Phase Power Transmission: triplex overhead wires are employed for the transmission of three-phase alternating current (AC) electricity, recognized for its high efficiency in power transmission. This particular arrangement facilitates the conveyance of greater power quantities through relatively thinner wires and at lower currents, thereby minimizing losses and enhancing overall efficiency, especially when contrasted with single-phase systems.
Load Balancing: In a three-phase system, the load is distributed evenly across the three wires. This balanced distribution helps maintain system stability, reduces voltage fluctuations, and enhances the reliability of the power supply.
Space Efficiency: The design of triplex overhead wires allows for a more space-efficient layout, requiring less physical space for the same transmission distance. This is particularly important in urban or space-constrained areas.
Reduced Copper Losses: The even distribution of current in a three-phase system reduces the heat losses generated by the current. This means that, compared to single-phase transmission, three-phase transmission can utilize electrical energy more effectively.
Extensions to overhead line cable systems require careful planning and execution. This includes assessing the capacity of the current infrastructure, determining the additional length required, and understanding the load impact of such extensions. Next, we can learn about the top security priority.

Are overhead electric cables dangerous?
The question of whether overhead electric cables pose a danger is multifaceted and warrants a thorough understanding, Overhead electric cables, by their very nature, carry inherent risks primarily due to their high voltage and exposure to environmental elements. Hazards arise in the case of poor maintenance, bad weather conditions or unexpected contact with cables. For example, a sloping or damaged cable can lead to electrical hazards that may cause power outages or power collisions. Additionally, cables exposed to extreme weather such as lightning, strong winds, or ice accumulation can lead to breakdowns or accidents.
Utilities and related departments must undertake regular inspections, carry out the necessary maintenance and inform the public about safety measures. For example, establish a safe distance, use warning signs in high-risk areas, and address any damage or wear in a timely manner. When these cables are properly installed, maintained, and compliant with rigorous safety standards, the risks are significantly minimized. Therefore, while overhead electric cables are inherently risky, adherence to safety protocols and regular maintenance can effectively manage and mitigate these dangers.
Conclusion
In the comprehensive landscape of electrical engineering, overhead electrical wires assert themselves as a critical component. Acting as the primary arteries of our electrical grid, these aerial lines span across vast distances, facilitating the reliable and efficient transmission of electricity from power generation plants to residential, commercial, and industrial establishments. As we advance into a future with an escalating need for robust and efficient power infrastructure, The role of aerial cables and overhead cable manufacturers will become increasingly important.
Among the variety of overhead lines available in the market, ZW Cable has carved a significant niche for itself, offering competitive overhead cable prices. We also offer a variety of overhead wiring for sale to meet different power transmission requirements and to withstand different environmental conditions. Our commitment to safety, quality and technical precision is reflected in every product we produce, thus earning us recognition in the field of overhead cable production. Moreover, The process of choosing, installing and maintaining an overhead wire requires deep understanding and expertise, and that is where ZW Cable stands out. so we can provide our customers with comprehensive guidance and support to ensure optimal performance and longevity of our products.
FAQs:
What is the minimum height for overhead cables?
For overhead transmission lines located above pedestrian-only areas, the minimum vertical clearance requirement between the line and the ground is typically 14.5 feet. This clearance standard is considered sufficient to ensure safe passage for all pedestrians. It takes into account the possibility that individuals may be carrying tools or various objects that could come into contact with the wires if the clearance is insufficient.
What is the difference between underground cable and overhead cable?
- Often supported by wooden poles or steel towers, overhead power lines are often used in rural areas because they can effectively span large distances. These lines distribute power across vast expanses of land, connecting remote areas to the grid.
- In contrast, underground cables buried beneath the surface are found primarily in environments such as cities. The use of underground cables in densely populated areas helps minimize safety risks and protects environmental aesthetics.
- Both systems play a vital role in the distribution of electricity, and each is suited to different geographic and environmental factors.