As a pivotal component in modern electrical systems, aluminum wiring is transforming the landscape of power transmission and distribution. We will explore this kind of aluminum cable in detail in our business blog, covering its benefits and drawbacks, current-carrying capacity, temperature variations, and the reasons it is utilized as an overhead cable. Whether you’re an industry professional seeking in-depth knowledge or a curious individual exploring your options, this guide to aluminum cable will provide valuable insights to aid your understanding and decision-making process.
What are types of aluminum cables?
Aluminum cables, known for their conductivity and lightweight, come in various types, each designed for specific applications and environments. Here’s an overview of the main types:
1.Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR): This cable features strands of aluminum and steel, combining strength and conductivity. It’s commonly used in overhead power lines.
 2.All-Aluminum Conductor (AAC): Made entirely of aluminum, AAC is lighter and more flexible than ACSR but less strong. It’s typically used in urban areas, where short spans and lower stress are the norm.
2.All-Aluminum Conductor (AAC): Made entirely of aluminum, AAC is lighter and more flexible than ACSR but less strong. It’s typically used in urban areas, where short spans and lower stress are the norm.
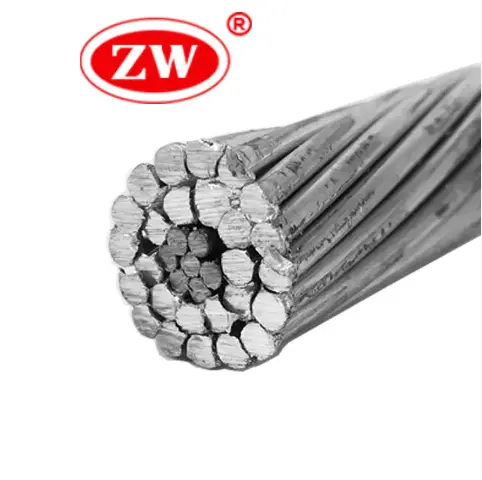 3.All-Aluminum Alloy Conductor (AAAC): Similar to AAC, but made from aluminum alloy for added strength without significantly increasing weight. It’s often used in overhead lines.
3.All-Aluminum Alloy Conductor (AAAC): Similar to AAC, but made from aluminum alloy for added strength without significantly increasing weight. It’s often used in overhead lines.
 4.Aluminum Conductor Alloy Reinforced (ACAR): This aluminium electrical conductor is made from a combination of aluminum and aluminum alloy, offering a balance between the strength of steel and the conductivity of aluminum.
4.Aluminum Conductor Alloy Reinforced (ACAR): This aluminium electrical conductor is made from a combination of aluminum and aluminum alloy, offering a balance between the strength of steel and the conductivity of aluminum.
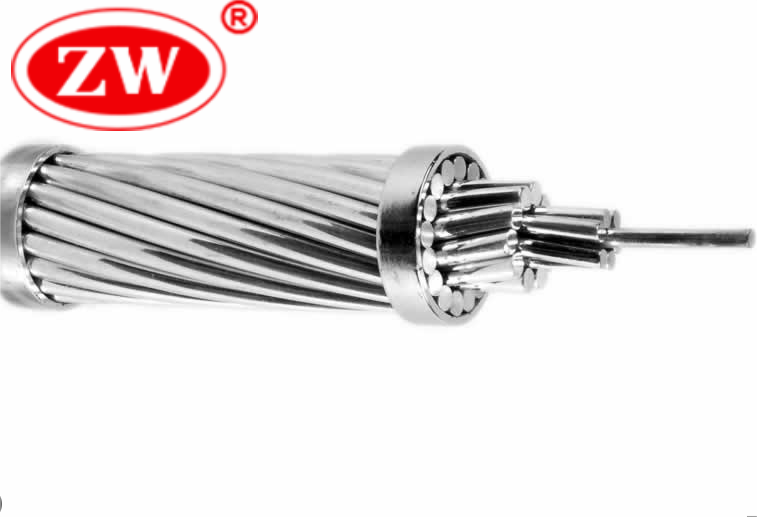 5.Aluminum Service Drop Cable: Used to connect the utility pole to the consumer’s premises, this cable often consists of AAC or ACSR and is usually insulated.
5.Aluminum Service Drop Cable: Used to connect the utility pole to the consumer’s premises, this cable often consists of AAC or ACSR and is usually insulated.
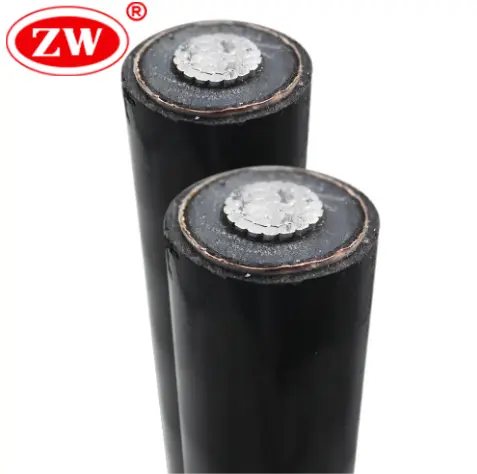

6.Aluminum Building Wire: Specifically designed for interior electrical wiring in homes and buildings, this type of cable is often insulated with PVC or other materials.

7.Aluminum Armored Cable: It is commonly used in applications where additional protection is required, e.g. 4-core armored aluminum cables can be used for power distribution in large buildings. The armoring provides additional protection against physical damage.
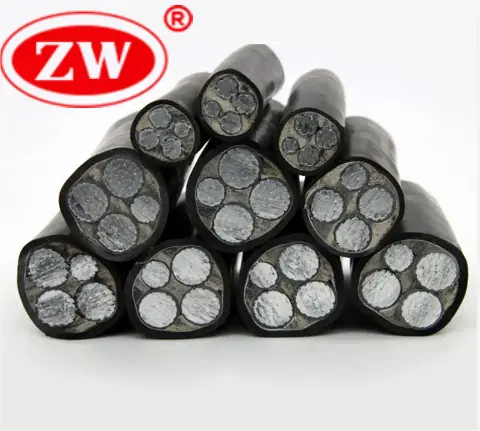 8.Aluminum Underground Cable: Specifically designed for underground or buried installations. These direct bury aluminum power wires are often insulated and sheathed with materials that resist moisture and physical damage.
8.Aluminum Underground Cable: Specifically designed for underground or buried installations. These direct bury aluminum power wires are often insulated and sheathed with materials that resist moisture and physical damage.
Remember that the type of aluminum electrical wire you require will depend on the application. When choosing wiring for particular applications, it is always advisable to seek professional advice or consult local codes and standards. Next, Let’s focus on the benefits and drawbacks of aluminum cables in more detail.
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum wire
Advantages of Aluminum Wire:
Lightweight: When comparing the lightweight of aluminum power cable to copper, the same length of copper or steel wire is significantly lighter. This makes it easier to transport and install, especially in weight-critical applications such as aerial wire.
Excellent Conductivity: Aluminum is one of the most conductive materials available. Its electrical conductivity is only surpassed by copper among commonly used metals, making it an excellent choice for transporting electrical current.
Cost-Effective: Aluminum is typically less expensive than copper cable, providing a cost-effective solution for many applications, especially those requiring large amounts of wire.
Corrosion Resistant: Aluminum exposure forms a protective oxide layer in the air, making it corrosion-resistant, especially in open-air environments.
Abundant and recyclable: Due to its abundance and ability to maintain quality, aluminum is a choice that is friendly to the environment.
Disadvantages of Aluminum Wire:
Oxidation at Connections: Oxidized layers on connections increase resistance and can cause overheating.
Lower Tensile Strength: Aluminum has less tensile strength than copper, making it more susceptible to damage from stretching or heavy loads.
Creep and Cold Flow: Aluminum can gradually deform under pressure, which can lead to loosening of connections over time.
Thermal Expansion: Aluminum expands more when heated than copper, which may cause the connection to loosen when the temperature fluctuates.
In conclusion, while aluminum wire has several important benefits, it’s important to be aware of its drawbacks in order to ensure efficiency and safety when utilizing it in electrical systems. Proper installation techniques and the use of appropriate connectors can help overcome many of these challenges.
What is aluminum cable current carrying capacity?
The current-carrying capacity of aluminum electric cables depends on a number of factors, including cross-sectional area (gauge), type of insulation, ambient temperature, and whether the cable is installed in free air or buried directly in the ground. It is of great importance to check the amperage meter in order to select the right size aluminum wire for the current requirements of the application. The following is an aluminum cable current carrying capacity chart for your reference:
| Nominal cross section of conductor | Current- carrying capacity | |
|---|---|---|
| (mm²) | in air | Underground |
| 25 | 110 | 110 |
| 35 | 130 | 130 |
| 50 | 155 | 150 |
| 70 | 190 | 185 |
| 95 | 235 | 225 |
| 120 | 270 | 255 |
| 150 | 305 | 285 |
| 185 | 350 | 320 |
| 240 | 410 | 375 |
| 300 | 470 | 425 |
| 400 | 550 | 485 |
An electrical aluminum current carrying capacity chart is a vital reference that aids in the safe, efficient, and cost-effective design and installation of electrical systems. The larger diameter cable can carry more current due to lower resistance. e.g.25 mm aluminum cable is rated at 110 amps; 120 mm aluminum cable rated at 270 amps in air and 255 amps underground. The temperature fluctuations of aluminum cables are yet another crucial element.
what is the change in temperature for the aluminum wire?
Temperature fluctuations can notably affect the electrical characteristics and functionality of aluminum wire. Below are some essential aspects to keep in mind:
- Current: The amount of electrical current flowing through the wire. The more current, the more heat is generated.
- Resistance: With an escalation in the temperature of an electrical aluminum, there is a corresponding rise in its electrical resistance. This phenomenon occurs as the wire’s atoms exhibit increased vibration at elevated temperatures, obstructing the electron flow.This can lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the electrical system and potentially cause overheating.
- Time:The duration of the current flow. Continuous current flow can cause the wire to heat up more than intermittent current flow.
- Wire Gauge (Diameter): A further consideration is the thickness of the When subjected to an identical level of current, wires with a smaller diameter demonstrate a quicker rate of heating and possess higher resistance compared to their thicker counterparts.
- Heat Dissipation: This concerns the speed of heat dispersion into the environment, influenced by factors like the conductor’s surface area, surrounding temperature, and availability of cooling airflow.
Temperature variations in electrical wiring should be kept within the safety limits indicated in the wire ratings in properly designed and operating circuits. However, temperatures can rise sharply in the event of overloads or short circuits, which could result in damage or fire. Therefore, the electrical installation should always be carried out by qualified professionals in accordance with local electrical norms and standards, while using protective devices such as circuit breakers or safety wire to prevent dangerous overload.
Why is aluminum used as an overhead cable?
Aluminum is often the material of choice for overhead power transmission and distribution lines due to its unique set of properties. Here are some key reasons:
- Aluminum is generally cheaper than copper. Given the large volumes of metal required for extensive power lines, the cost difference can result in substantial savings.
- Its lightweight nature reduces infrastructure costs by allowing longer spans between support structures.
- The corrosion resistance of aluminum armored cable makes it suitable for outdoor applications.
- Aluminum’s good electrical conductivity makes it suitable for transmitting electricity over long distances.
- Aluminum has a high thermal conductivity, which means it can effectively dissipate the heat generated from electrical resistance. This is especially useful in aerial electrical cables where air cooling can assist in heat dissipation.
 However, it is important to note that al wire requires special handling and connectors to accommodate its properties, such as creep tendency and coefficient of thermal expansion. For overhead conductors, aluminum is often used in combination with a steel core to provide additional strength and prevent sagging.
However, it is important to note that al wire requires special handling and connectors to accommodate its properties, such as creep tendency and coefficient of thermal expansion. For overhead conductors, aluminum is often used in combination with a steel core to provide additional strength and prevent sagging.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving world of electrical cabling and power transmission, aluminum cables have carved out a significant niche. Aluminum cable prices are stabilized and suitable, their lightweight nature, high electrical conductivity, and robust corrosion resistance make them a top choice in a variety of applications, especially aerial cable. Understanding their current carrying capacity and temperature changes under operation is essential for their safe and efficient utilization. Despite certain challenges such as thermal expansion and lower tensile strength, proper installation techniques can effectively address these issues.
To sum up, there are a lot of prospects for electrical aluminum in the electrical industry because of its special benefits and broad range of applications. Manufacturers such as ZW Cable are spearheading the advancement of aluminum wiring goods. We provide a variety of aluminum electrical cable products to meet various needs that guarantee not only efficient power transmission but also a balance between powerful performance and affordability.
FAQs:
Why is aluminium cheaper than copper?
Copper costs significantly more than aluminum. This is mainly due to copper’s higher electrical conductivity and efficiency. Copper is much more flexible and easier to process than aluminum. In addition, the supply of copper is decreasing. A large portion of the global copper supply goes to China. This scarcity and high demand for copper has resulted in copper being more expensive than aluminum and poses additional challenges.