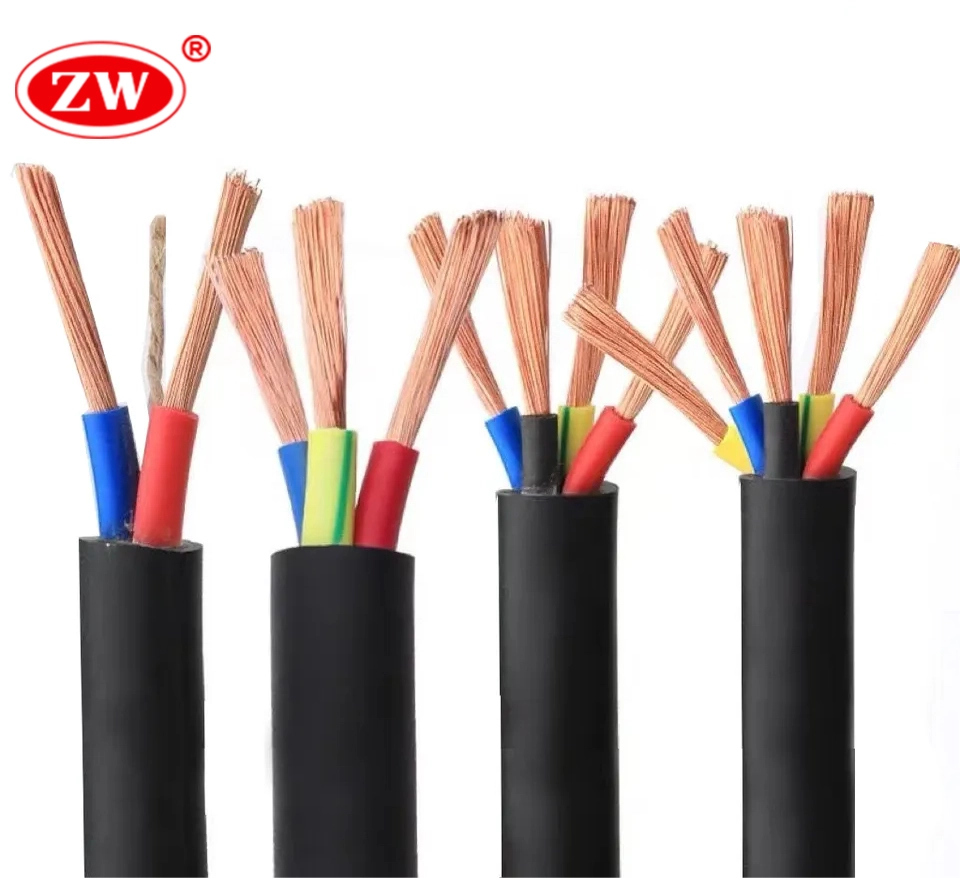
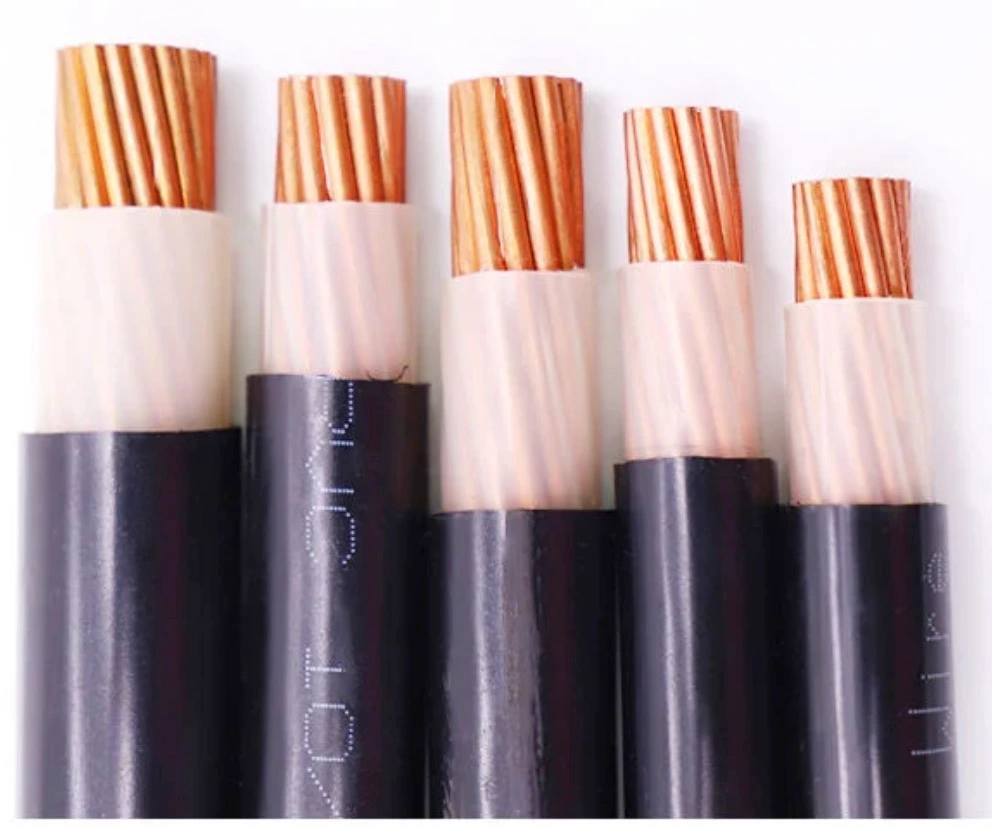
Low voltage(lv) cable is a common type of electrical cable designed to transmit electricity, current or signals at low voltage levels. Distinguished by the voltage level, electrical cable can be divided into low voltage cable, medium voltage cable and high voltage cable, LV cable can withstand the voltage of 0.6kv/1kv and is able to enter the field of long-distance power transmission. Let’s take a detailed look at low voltage cables.
What is low voltage cabling?
Low voltage cabling refers to the installation of electrical cables at lower voltage levels. It is typically used for house wiring, network connections, data transfer, and communication systems. Low-voltage cabling employs a structured cabling architecture, which offers convenience fo the cable installation, management, and maintenance. When wiring low voltage cable, it is critical to understand the proper installation, which is related to signal integrity, interference protection, and safety. The standard conductor material for low-voltage cable is copper or aluminum, and covered with XLPE insulation and PVC sheath. Since low-voltage cables are essential for enabling communication, connectivity, and automation in various situations, people must become familiar with low-voltage systems and the many types of low-voltage cables.
What are Low voltage cable types?
There are several low voltage cable types, each designed for specific purposes in different applications. Here are some common types of low voltage cables.
PVC insulated Cable
PVC (polythene) insulated cable is a type of low voltage cable ,that refers to the use of PVC material for the insulation wrapped with conductor. PVC material has good electrical properties such as flexibility, making it easier to bend the cable for wiring in tight spaces. Moreover it is moisture resistance, making the cable better suited to the environment.

PVC insulated cables can withstand a maximum of 90 degrees Celsius and are available in different colors for people to differentiate and identify them. Generally, PVC insulated cables can be used to wire low-voltage systems, such as inside buildings, to help distribute power and control circuits, which can be single-core, multi-core, and twisted and is cost-effective to produce. Special consideration should also be given to the specifications for using PVC insulated cables.
XLPE Insulated Cable
XLPE insulated cable means that the cable is insulated using xlpe material as the conductor. XLPE is a thermoset polymer with good thermal stability, moisture resistance and chemical resistance, and can withstand temperatures up to 120°C, allowing the cable to operate effectively even under high temperature conditions. At the same time, XLPE is also resistant to UV radiation, giving the cable a longer service life and minimizing the loss of signals and power during transmission.

XLPE is an environmentally friendly material that reduces the smoke emissions from the cable when a fire occurs. XLPE insulated cables are mainly used in industrial, underground, and other long-distance transmission of power and signal occasions, which can more effectively keep the cable running smoothly. XLPE insulated cables have high installation requirements, and people must refer to the wiring requirements when installing the cable.
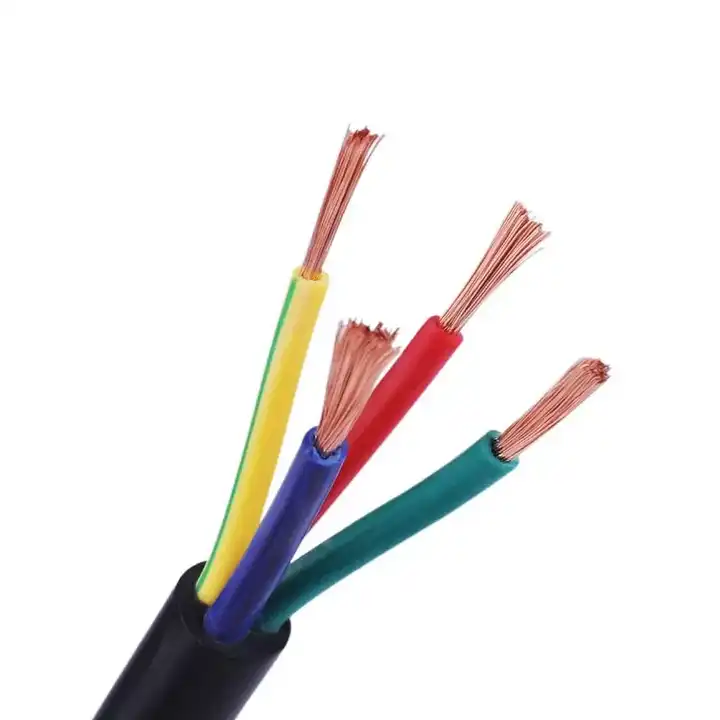
Flexible Cable
Flexible cable, as the name suggests, refers to a highly flexible low-voltage cable that supports repeated bending and twisting without damaging the conductors during installation. The conductor of a flexible cable is made up of several thin wires that are twisted together to provide mobility, flexibility, and durability. Flexible cables are usually sheathed to protect the conductors and insulation to be resistant to abrasion and chemicals.

Flexible cables are frequently used in low-voltage lighting, sound equipment, automation equipment, medical diagnostic equipment, aeronautical equipment, and other applications that require great cable flexibility. Although flexible cables are incredibly flexible, it is important to pay attention to the low-voltage cable specifications when installing them to ensure that the electrical cables run safely and properly and to prevent over-bending or stretching, which might reduce the electrical performanc
LSZH Cable
LSZH cable refers to Low-Smoke and Halogen-Free cables, which are insulated with low-smoke and halogen-free materials to emit very little smoke and halogen gases in the event of a fire that are harmful to humans and equipment. LSZH cables are suitable for enclosed spaces or areas with limited ventilation, such as public buildings, transport systems, and basements, where the emission of smoke is critical. In addition, LSZH cables maintain visibility in the event of a fire, allowing for better evacuation of people.

Moreover, LSZH cable also belongs to the category of cables made of environmentally friendly materials aligned with fire safety and environmental norms. The choice of LSZH power cable depends on the local norms, environmental conditions, and budget, and people can consult a professional electrician.
Mineral-Insulated cable
Mineral insulated cable can also be named MI cables or mineral-insulated metal cables (MIMC). This type of low voltage cable consists of a conductor made of metallic materials (copper, stainless steel, etc.) and a highly compressed insulation made of magnesium oxide material wrapped in a metallic sheath. This construction gives mineral-insulated cables good fire resistance, durability, high insulation, etc. MI cables are generally used in defense, petrochemical facilities, and power plant applications, where the signal is kept intact, and the cables are arbitrarily resistant to mechanical damage, chemical attack, and abrasion.

Since magnesium oxide material is non-flammable, this cable can also withstand high temperatures and flames. Mineral-insulated cables are expensive to produce and are more commonly used in extreme conditions. Consult an experienced electrician for installation.
What is benefits of low voltage cable?
Low voltage cables have several advantages that make them popular choices for various applications. These benefits include energy efficiency, safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Safety:Low-voltage cables are the best choice for handling and installation, as they significantly reduce the risk of electrical shocks and fires. They are used in both residential and commercial environments where safety is a top priority.
- Energy Efficiency: Low-voltage cables can be more energy-efficient for certain applications, particularly in low-power tasks such as lighting or small electronics, leading to lower energy costs over time.
- Cost-Effective Installation and Maintenance: Low-voltage systems often require less expensive materials and can be easier to install and maintain due to the reduced complexity and safety hazards.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Low-voltage cables can offer greater flexibility in terms of installation and future expansion. Systems using low voltage cables can be easily scaled or modified to accommodate changing needs or technologies.
- Reduced Regulatory Requirements: Since low-voltage cables pose less risk, installing and operating low voltage systems often face fewer regulatory hurdles, simplifying compliance.
Low voltage cables can lower energy consumption and associated costs by reducing the amount of voltage required to operate electronic devices or power systems. In addition, they are generally more durable and reliable than traditional high-voltage cables, which can minimize maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Does low voltage cable need to be in conduit?
The conduit plays an important role in installing low-voltage cables. The purpose of the conduit is to provide the cable with physical protection from the elements, such as animal bites, mechanical damage, and moisture. The conduit fills for low-voltage cables are determined by many factors. In some cases, low-voltage cables need to be installed in conduit to protect the cable.
- Environment:To guarantee the cable’s smooth operation, conduits for low-voltage cables must be installed if low voltage cable wiring is to be done in challenging conditions or busy locations.
- Fire Protection:Certain conduits constructed of unique materials canprevent fires, safeguarding the cables and adding to security in the event of a fire.
- Distance:When wiring low voltage cables over long distances, conduits are required to avoid damage to the cables over long distances.
- Maintenance:Installation of low voltage cable using conduit is conducive to keeping them in order. When carrying out cable maintenance, it is convenient for people to identify and distinguish between cables and replace them in a targeted manner.
Since some areas consider safety issues, cables are required to be installed in conduit to comply with local regulations. Furthermore, low-voltage cable manufacturers provide some information about suitable cable solutions and you can refer to their advice. Finally, let’s analyze whether high voltage and low voltage cables can be run together.
Can low voltage and high voltage cables run together?
We do not advocate running low voltage cables and high voltage cables together for safety, signaling, and anti-interference reasons. Here are the specific analyses.
Firstly, as high-voltage cables carry far more power than low-voltage cables, if they are run together, the high-voltage cables are accompanied by low-voltage cables in the event of a fault, posing an even greater danger to workers.
Secondly, the electromagnetic field and noise produced by the high-voltage cable interfere with the low-voltage cable, disrupting the signal and electricity transmission and steady operation of LV cables.
Thirdly, low voltage cables have a rated voltage of 0.6/1kV, while high-voltage cables have a voltage rating of 66kV/110kV. The voltage difference is too great to run them together.
Finally, high-voltage cables are more likely to catch fire in the event of a short circuit or other malfunction, which can harm low voltage cable, paralyze the nearby circuits, and pose other problems.
Consequently, low voltage cables and high-voltage cables cannot run together. During low voltage cable installation, it is important to maintain a safe distance or take precautions such as isolating and shielding to ensure safety and non-interference.
Low Voltage Cable Conclusion
Our blog aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the various types and definitions of low voltage cables. In this way, the project manager can choose the best low voltage cable that meet their specific requirements to provide an economical and safe solution.
ZW Cable offers a wide selection of high-quality low-voltage cables at competitive prices. Our LV cables are made from high-quality materials and adhere to industry standards, ensuring reliable performance and durability. Additionally, we provide customizations for extra low-voltage cables to meet specific application requirements, ensuring a satisfactory customer purchasing experience.