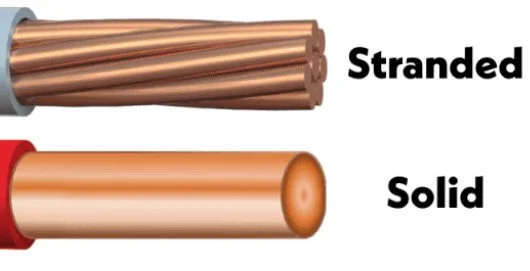
Copper cables are highly desirable. cu cables transport the currents and signals that keep the world going, serving as the heartbeat of the global data and power network. However, what exactly is copper cabling and why is it utilized in so many different industries? Now let’s explore the realm of copper wires.
What is a Copper Cable?

Copper cable is a type of electrical cable that has conductors made of copper. Copper is widely used in cables due to its excellent electrical conductivity, flexibility, and durability. Here are some key aspects of copper cables:
High Conductivity: Copper is one of the best conductors of electricity, surpassed only by silver. This makes copper cables highly efficient for transmitting electrical power and signals.
Flexibility: Copper is a ductile metal, meaning it can be easily bent and shaped. This property makes copper cabling suitable for a wide range of applications, where cables need to be routed through tight spaces or around corners.
Durability: Copper is resistant to corrosion, which extends the life of the cable. It can also withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Insulation and Sheathing: Copper cables are often insulated and sheathed with materials like PVC, rubber, or Teflon to protect against environmental factors and to ensure safety.
Electrical Properties: Cu cables have unique electrical properties that affect how well they function in various applications, including resistance, capacitance, and inductance.

What is Copper Wire Used For?
Copper electrical wires are exceptionally versatile and have a wide range of uses owing to their superior electrical conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Power Transmission and Distribution: Copperwires are often used in electrical power infrastructures to transport electricity from power generating facilities to residential buildings, commercial buildings, and other locations.
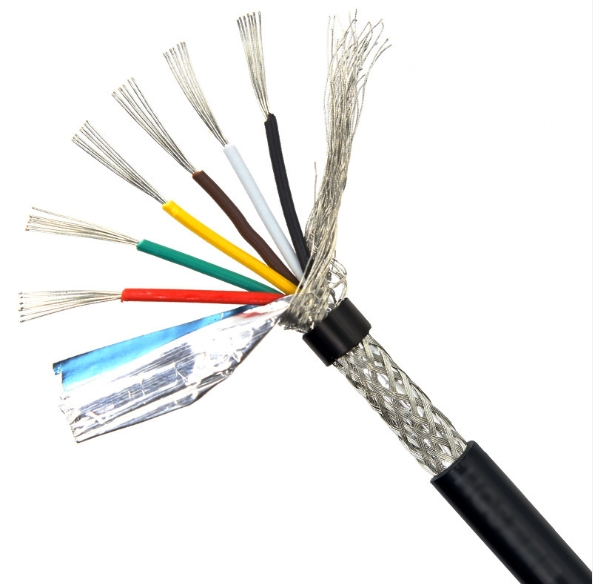
Telecommunications: Voice and data signals are transmitted over telephone lines using copper wire and cable. They are also used in broadband and Ethernet cables for internet connections. Furthermore, copper cable color codes are typically identified in the networking and telecommunications sectors.
Audio and Video: The wire of copper is used in audio and video equipment for signal transmission. This includes speaker wires, HDMI cables, and more.
Automotive Industry: Single core copper cables are utilized in cars for a variety of electrical systems, including the alternator, starter motor, and data buses for electronic controls. They are also used as power and grounding wires.
Remember, despite their versatility, cu wires should be installed and maintained properly to ensure safety and performance. Always comply with local regulations and industry standards when using conductor copper. Thus, we are now able to evaluate in more detail whether copper is a good electrical conductor.
Is Copper a Good Electrical Conductor?
Absolutely! Copper is one of the best conductors of electricity. When deciding between copper and aluminum wires, conductor copper is superior at conducting electricity due to its higher electrical conductivity. Thus, this accounts for a portion of the higher cost of cu wires. Similarly, The high purity of oxygen free copper makes it an excellent conductor of electrical signals. It can also be used in applications that require a higher degree of conductivity.
Businesses that depend on dependable and quick data transmission will find it ideal due to its exceptional conductivity, which enables it to transmit signals with little loss. Furthermore, copper is widely used in the electrical industry due to its strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. In addition, we can also learn about the types of cu cables.
Different Types of Copper Cables
Twisted Pair Copper Wire
A twisted pair cable is a cable consisting of two copper wires twisted together. Twisted-pair cables help to minimize electromagnetic interference between adjacent pairs of wires. They are commonly used in telecommunications and computer networks because they can transmit data over long distances with minimal interference.
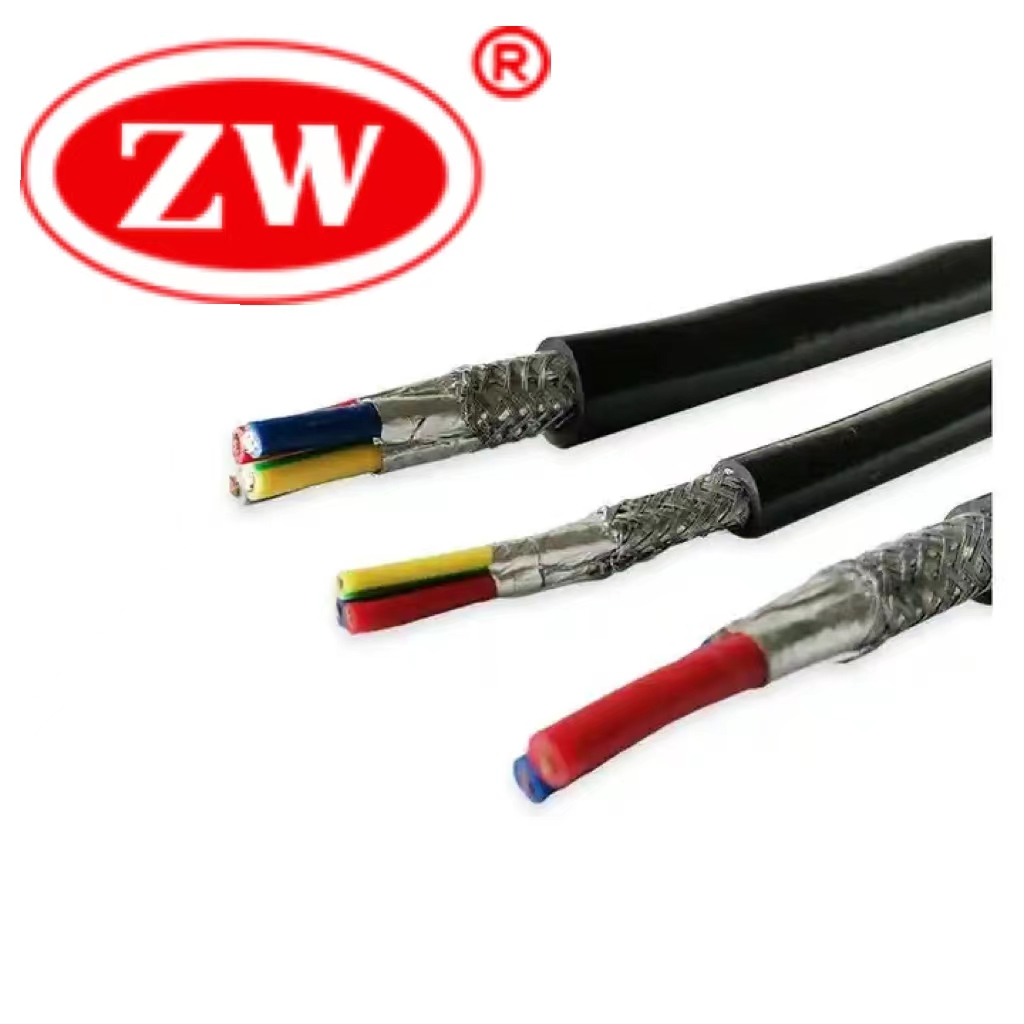

Copper Electrical Cable
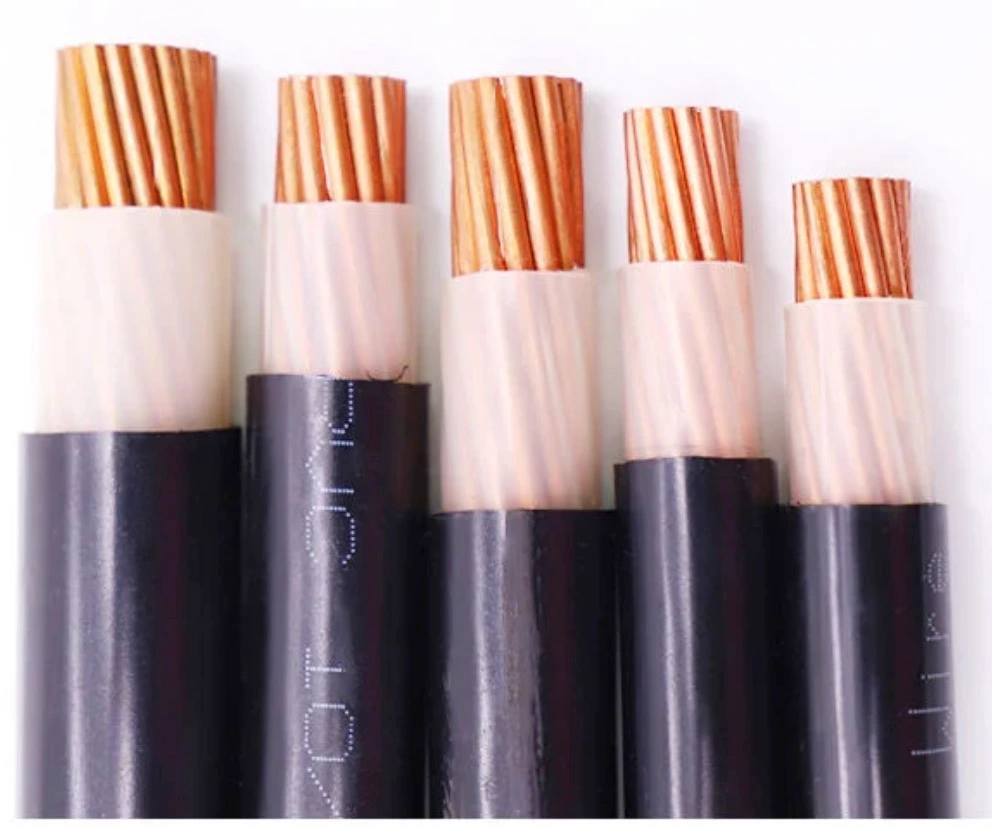
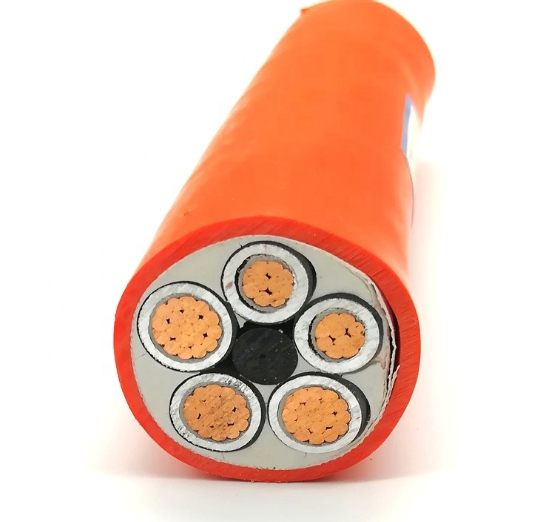
This broad category has armored cables and high voltage copper cables. Armored copper cables are used in environments where cables need extra protection, like underground or in buildings’ walls. High voltage cu cables are designed to handle heavy electrical currents and are primarily used in power distribution networks.
Braided Copper Wire
Braided copper wire is a specific type of conductor that is widely used in various electrical and electronic applications. It consists of numerous small strands of copper wire braided together to form a flexible and sturdy conductor.
The surface of insulated copper wiring is covered in an insulating layer that shields it from harm, lowers the chance of electrical fires, and stops electric shocks. In wiring for homes, businesses, and industries, insulated copper wiring is frequently utilized. Our common types of insulated wires are house wire, flexible cable, and control cable.
copper coaxial cable
Coaxial cable consists of a physical channel that carries a signal surrounded by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis. It can be used to transmit both analog and digital signals and is commonly used for broadband Internet connections, cable television and radio transmissions.
copper cabling comes in various varieties, each suited for a particular use. Next we can discover the precise manufacturing process for them.
How is Copper Wire Made?
The manufacturing of copper cable involves several key steps, transforming raw copper into a versatile and widely used electrical conductor. Here’s an overview of the process:
1.Mining and Extraction: Cu wire production begins with the mining of copper ores. These ores are then refined to extract pure copper. Copper is usually found in nature mixed with other minerals and materials. Through processes like smelting and electrolysis, copper is purified to a level suitable for electrical uses.
2.Casting: The purified copper is melted and cast into large, thick rectangular slabs or billets. These billets are the starting material for making copper conductors.
3.Hot Rolling: The copper billets are heated and passed through a series of rollers in a hot rolling process. This step reduces the thickness of the copper, forming it into a long, thin length. The copper may be hot-rolled multiple times to achieve the desired diameter.
4.Cold Rolling and Annealing: After hot rolling, the cu wire undergoes further thinning through cold rolling, where it is not heated. This process improves the strength and hardness of the wire. The wire is then annealed, a heat treatment process that softens the metal, restoring its ductility. Annealing is crucial for making the wire flexible and suitable for applications that require bending and shaping.
5.Drawing: The annealed copper cable is then drawn through a series of progressively smaller dies to further reduce its diameter and achieve the desired gauge (thickness). This process, known as wire drawing, requires the copper to be both strong and ductile. Lubrication is often used during drawing to reduce friction and prevent damage to the wire.
6.Stranding (for Stranded Wire): If stranded cu cables are being produced, multiple thin wires are twisted or braided together. This increases the flexibility of the wire, making it suitable for applications where the wire needs to move or flex.
Where to Buy Copper Wire?
Do you know where you can get wires for your upcoming electrical project? It is well known that quality cables are essential to ensure the proper functioning of equipment and systems. Not only should how much copper wire costs be taken into account when selecting a trustworthy cable company, but also whether the product satisfies quality standards and can withstand long-term use in various environmental conditions. Therefore, the selection of copper cable manufacturers for sale should consider whether it is up to standard.
We can better appreciate the vital role they play in our globally interconnected world by being informed of their types, uses, and manufacturing processes. It also becomes the foundation for the decisions we make. Furthermore, as an experienced cable manufacturer, ZW Cable will also provide you with appropriate answers to any questions you may have regarding the color coding of copper cables. Please get in contact with us without holding back!
FAQs
What are the disadvantages of copper wire?
When used for electrical purposes, copper wires can generate electromagnetic interference that can seriously disrupt signal quality. This interference not only affects the stability of the connection, it can lead to unpredictable performance and connection problems.
Is copper cable 100% copper?
Pure copper, also known as electrolytic copper, is produced by an electrolytic process. This method ensures the highest quality copper, with a purity of over 99.95%. This purity provides maximum electrical conductivity.