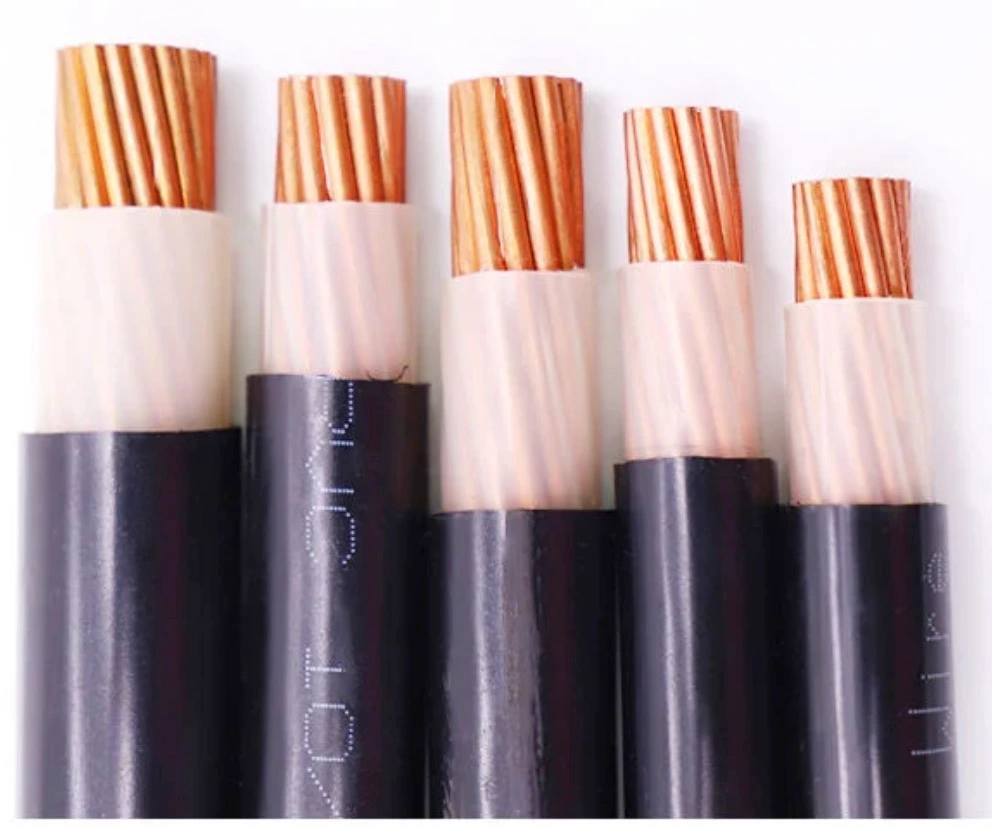
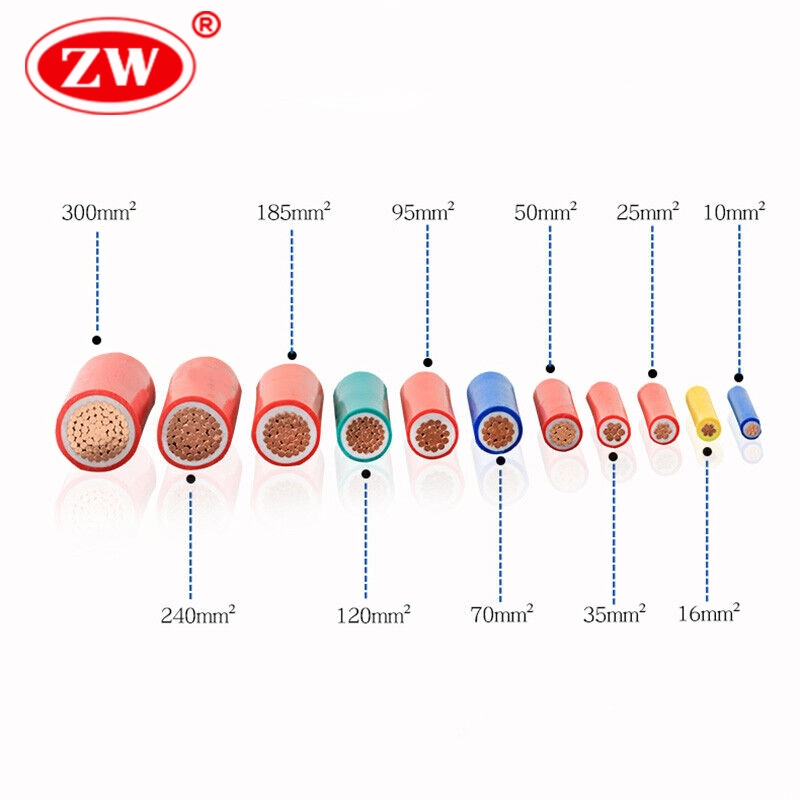
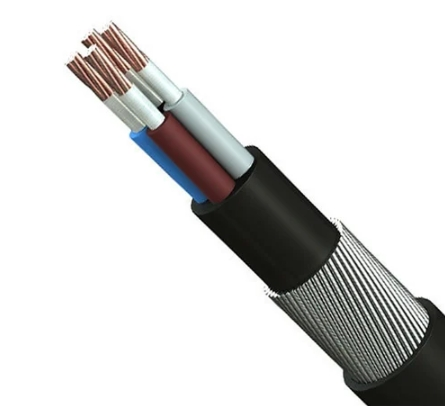
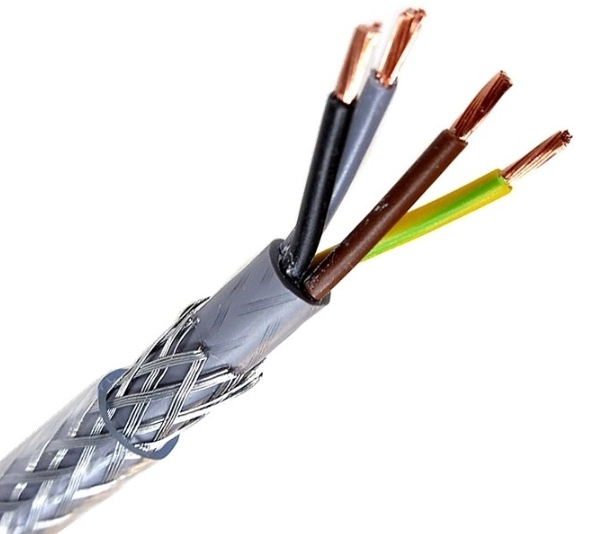
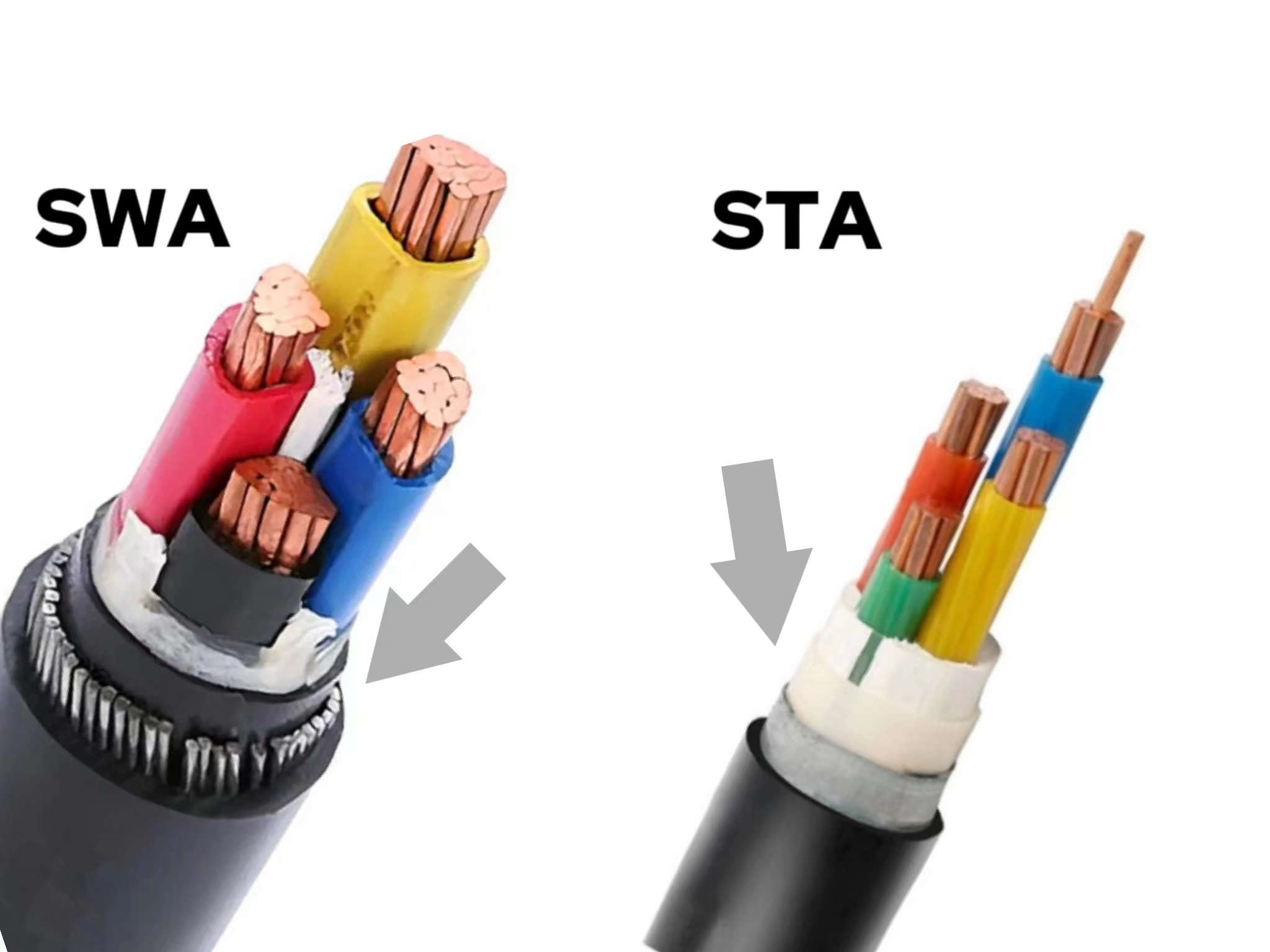
Electrical cables transmit and distribute electrical power in various applications. Different electrical systems and wiring environments use different electrical cable types, so we need to fully understand the electrical cable types so that people can use electricity safely.
In this passage, I will lead you to understand the electrical cable types, sizes, installation and wiring environment of cables, etc., to help people choose more suitable cables.
What are the different electrical cable types?
There are many different electrical cable types in various applications. We use cable for electricity to accomplish our goals. Below is the electrical cable types list.
Low Voltage Cable
Low voltage power cable is also called LV cable; low voltage cable comprises a conductor, insulation layer and sheath. Its rated voltage is 0.6-1.0kv because it has reliable, current operation, does not occupy the ground and is less affected by the external environment characteristics, so it is widely used in low-voltage power distribution systems, such as construction engineering, family residences, and commercial construction, etc.

Flexible cable
Flexible cable’s sheath varies from the sheath of other electrical cable types. It utilizes flexible and wear-resistant materials to reduce the wear and tear caused by the cable during use. Flexible cables are soft, changeable and have strong coordination capabilities. They are typically employed in intelligent applications such as robotics, automation, and equipment. Due to the particularity of the flexible cable itself, the cable drag chain should be used to protect the cable when installing and wiring, but it should be noted that the cable cannot be twisted or forced to move at will.

Control Cable
Control cable refers to the power connection line that is directly transmitted from the distribution point of the electrical system to various electrical equipment. The control cable’s PVC insulation and sheath are thinner than those of other electrical cable types, and it has the features of moisture resistance, corrosion resistance, and damage resistance. Its rated voltage is 450v/750v. Thus it can wire in tunnels, indoors, pipelines or the cable trench. The long-term permitted operating temperature of the control cable conductor is 70℃, and the cable laying temperature is above 0℃.

Rubber Cable
Rubber cable is insulated and sheathed with rubber or elastic materials, so it can also be called rubber-insulated cable. It is characterized by softness and durability because of its material. Rubber cables are suitable for use in harsh environments that often suffer wear and corrosion, such as construction, mining and manufacturing. Moreover, it is also used in residential construction as extension cords.

Battery Cable
In daily life, people use battery cables frequently for automatic vehicles, RVs, and solar systems. Battery cables’ task is to transfer electrical power from the battery to the electrical system of a device or vehicle, enabling efficient power transfer. When we use the device, the battery cable will carry a large amount of current to support the startup and operation of the device, so people must ensure that its wiring and connection are correct, but over time, the battery cable will be damaged by corrosion, so people need to check and replace it regularly to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.

Halogen-free cable
Halogen-free cable refers to cables that cables not containing halogen materials in the cable manufacturing structure. Halogen includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and Isida, which are typical salt elements. Compared with other types of cables, Halogen-free cable has very low smoke emission when energized and heated, and even when it is on fire, it will not produce toxic, corrosive acid gases. In poorly ventilated environments such as ships, airplanes, train carriages, and public buildings, halogen-free cables are used to reduce smoke emissions and short circuits or fires and protect people from exposure to toxic gases. At the same time, halogen-free cables are often used in firefighting to reduce the spread of flames and smoke emissions and ensure fire safety.

Medium Voltage Cable
Medium voltage cable is referred to as mv cable for short. The rated voltage is higher than that of low-voltage cables, which is 3.6kv-35kv and can transmit higher currents. Medium voltage cable is composed of copper or aluminum as a conductor, plus an insulation layer, shielding layer and sheath to protect the current of long-distance cable and minimize loss. They’re mostly used outdoors or in pipelines and can be buried underground or erected in the air. Due to the medium-voltage cables’ higher voltage, people must pay special attention to installation correctly, comply with the standards of the related electrical department, and follow requirements during wiring; take regular inspection and replacement into account during installation to reduce risks and ensure safety.

Humans own so many wire and cable types to use they can offer people convenient life. We use types of cable in the power system to light, cook, make the home smart and lots of applications that save workforce and material resources. However, during wiring, installation and use, To consult a professional electrician, comply with the local wiring and electricity requirements, and reduce the risk of electricity use.
So next, we can learn the electrical cable types sizes and installation so that we can choose the right wire and cable later.
Electrical cable types sizes and installation
The application scenarios of different types of wires with their specification are different, the electrical cable types sizes involved are also dissimilar, and the current consumed by different sizes are also not like. The table below is a description of it.
| Nominal cross-sectional area(mm²) | AWG | Current consumption | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 16 | Low | Low-power lighting and small appliance |
| 2.5 | 14 | Under | General power circuits |
| 4 | 12 | Medium | Kitchen appliances |
| 6 | 10 | Medium | Electrical water heater |
| 10 | 8 | Medium high | Outdoor power outlets |
| 16 | 6 | High air | Marine and vehicle |
| 25 | 4 | Very high | Solar power systems |
Now, you may need clarification about the difference between wire and cable. Next, we can talk about it.
Difference between wire and cable
The difference between wire and cable is mainly reflected in the following factors:
- Structure: The wire is usually composed of single soft conductors, and the outer layer is wrapped with a light and soft sheath, while the cable is composed of one or more conductors, plus an insulating shield and tough outer layer.
- Distance: The wire is used to transport networks and telecommunications over short distances while the cable is used for long distances.
- Voltage: Compared to the cable, the rated voltage of the wire is lower than the cable.
- Application: Wires are typically used for small electrical application connections, while cables are commonly used for medium or high-voltage application connections.
Above are the difference between electrical wires and cables. When selecting wire or cable, people must consider these factors and then acquire a suitable type of electrical wire.
So what are the electrical cable types that can be buried?
What type of electrical cable can be buried?
Buried cables are conditional; not all types of power cable can be buried. The following is the wire and cable types that can be buried.
Direct Burial Wire: It is a type of outdoor electrical cable and direct burial underground without conduit protection. With the addition of an armor layer, it can withstand ground pressure, soil corrosion, and rat bites. Directly buried wires will be restricted by local electrical codes. When people use it, they need to be tested to make it a qualified direct buried wire.

Underground Service Entrance (USE) Cable: USE cable is made up of several conductors with insulation and bare copper earth wire. And used for underground electrical service connections for residential, commercial buildings, and public areas.
Underground Feeder (UF) Cable: It can also be referred to as a branch circuit cable and is commonly used in outdoor electrical installations. And UF cable is constructed like USE cable, specifically designed to bury.
Quadruplex & Triplex Direct Burial Aluminum Underground Distribution Cable: It consists of multiple aluminum conductors wrapped in xlpe insulation and is also used in residential and commercial applications.
When burying these residential electrical cable types, pay attention to the requirements for underground burial and comply with the electrical codes of relevant local departments to ensure a safe, reliable and stable underground power distribution system.
Then let’s acquire knowledge of electrical cable types and applications.
Electrical cable types and applications
Below is the introduction of 3 types of cable applications and features:
1. Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable (NM)

Application: Non-metallic sheathed cable is generally used for indoor sockets, switches, and lighting. It is cost-effective and suitable for indoor wiring.
Features: It is flexible, compatible with various equipment, cost-effective and efficient, and easy to install.
2. Armored Cable (AC)

Application: Armored cable is mostly used in harsh environments, such as outdoor, underground, commercial and industrial areas.
Features: Strong and durable, flexible and moisture-resistant, good compatibility and suitable for ground burial.
3. High Voltage Cable(HV)

Application: High voltage cables can be used for long-distance power transmission, connecting different substations. High voltage cables are used in projects such as industry, renewable energy projects and railways.
Features: Better electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, the shielding layer can prevent electromagnetic interference, withstand poor environments, and has strong fire resistance.
These are the applications and features of different electrical cable types, which we can have a further understanding.
Conclusion
Above all guidance, we can learn about electrical cable types, and know some underground electrical cable types, gauge, applications and features. So people will have a certain degree of understanding about different type of electrical wire, and then select the electrical cable types you want more clearly.
Attention, selecting and installing electrical cables requires consultation with local professional electricians and relevant departments and compliance with electrical requirements and specifications for correct installation and safe use in the future. At the same time, you can also consult us, and ZW Cable will give you corresponding solutions to choose from.