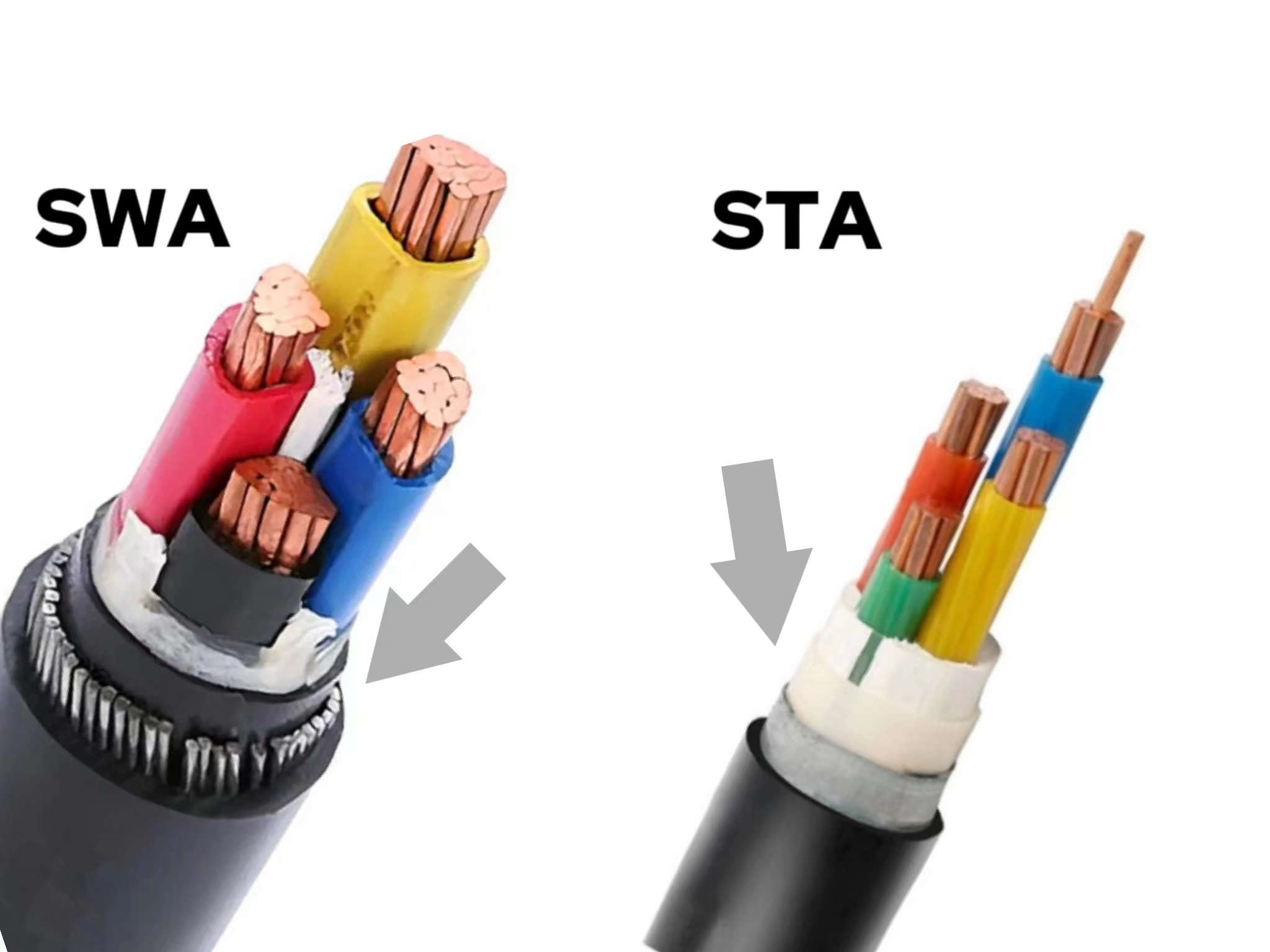
At the heart of the vast electrical grids that crisscross our cities and traverse entire continents are high voltage cables (HV cables). They transmit massive amounts of electrical energy over long distances to power constructions, industries, mines, etc., shaping our daily lives.

In this article, we will uncover the high voltage cable, including the definition, types, and sizes, as well as how to identify and connect them. Now let’s dive into the topic.
What is high voltage cable specification?
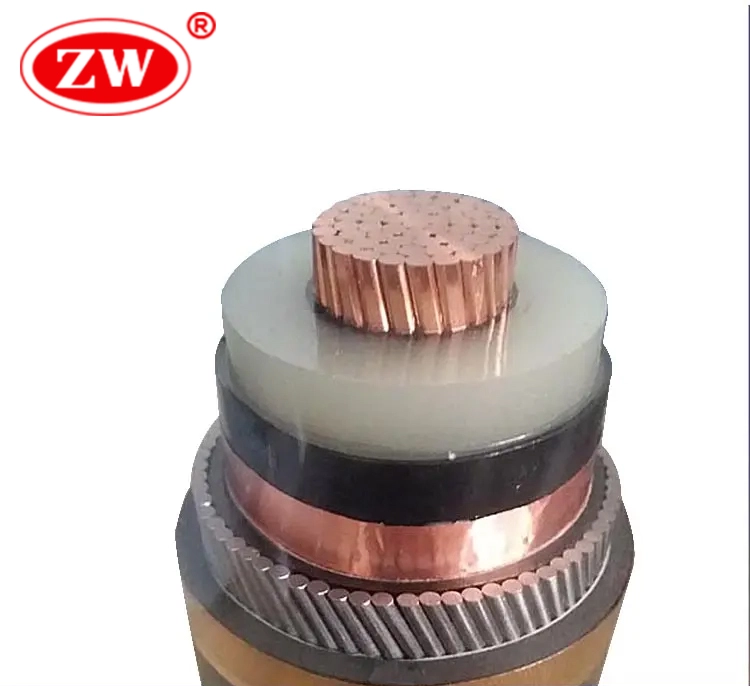
High voltage cable is a specialized electrical cable used to carry electricity at elevated voltage levels than normal cables while ensuring safety, reliability, and efficient transmission. Characterized by the ability to withstand extremely high electrical stress and voltage levels, which are usually 64/110kV and below; above 110kV for ultrahigh voltage. Due to the high electric field strength and low capacitance associated with the single conductor, high-voltage cables are usually in this configuration, and 69 KV and 110 KV cables are commonly used.
Compared to LV and MV cables, HV cables have a more complex structure with more layers, containing triple co-extruded insulation and shielding layers, and the structure from the inside out is generally stranded copper or aluminum conductors – warping tape – conductor screen – XLPE insulation – insulation screen – buffer layer – metallic sheath – armor (optional) – outer sheath. It is this robust construction that makes high voltage cables highly resistant to physical stress, corrosion, abrasion and moisture.
High voltage wires are the essential components of power transmission and distribution systems, such as power generation, substations, renewable energy projects, industrial facilities, etc..; these wires facilitate the connection between power sources and the grid, enabling the efficient distribution of electricity to end-users. The advantages of large transmission capacity, good electrical performance, and simple laying and installation make HV cable widely used in today’s power systems, and it is crucial to ensure a stable and efficient power supply for modern power infrastructure.
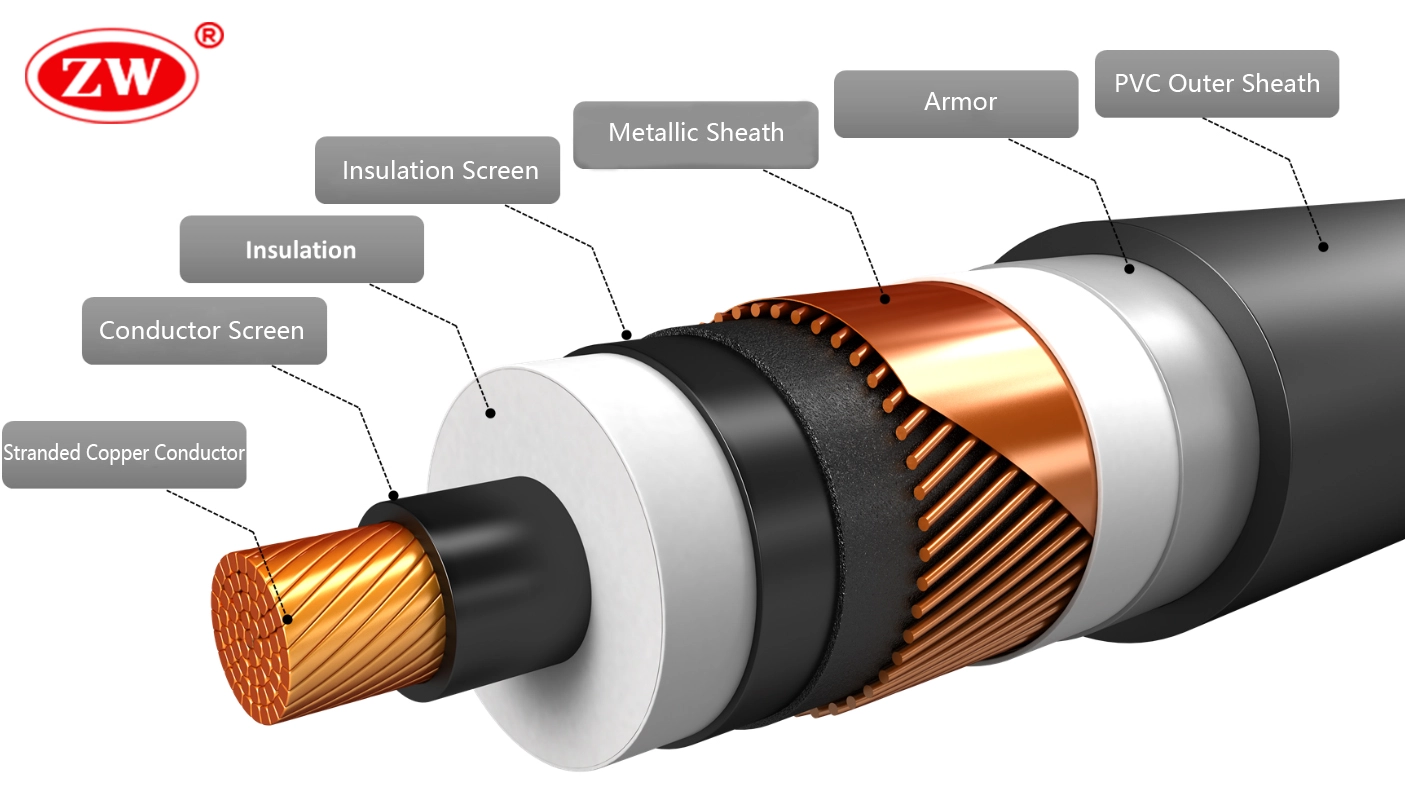
While high voltage cable specifications lay out the technical details and performance characteristics, in practice, high-voltage cable comes in a variety of types based on these specifications.
Types of high voltage cables.
High voltage cables are typically categorized based on factors like voltage ratings and specific needs, with each type having its unique design and configuration. Listed below are the most common high voltage cable types:
- High-Voltage Power Cable: For transmission and distribution of 69kv-110kv high voltage power.
- High-voltage coaxial cable: is designed to transmit high-voltage electricity while minimizing the risk of electrical interference, and is available in multiple materials, including silicone, polyethylene, EPR, XLPE, and PTFE; typically configured as shielded and unshielded cables. In high-voltage applications, some high-voltage coaxial cables can supplant standard 50 RG316 or RG213 coaxial cables.
- High voltage underground cable: transmits and distributes electricity over long distances underground, with voltages ranging from 36 kV to 230 kV. They are common in urban areas where overhead lines are impractical or unsightly.
- Extra-High Voltage (EHV) and Ultra-High Voltage (UHV) Cable: are designed for long-distance and accommodating exceptionally high capacities. EHV cables can carry electrical currents above 230 kilovolts (kV), while UHV cables are designed to handle currents surpassing 800 kV.
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Cable: HVDC cables are engineered to efficiently transfer high voltage direct current over extended distances while minimizing energy losses. These cables play a crucial role in improving grid connection and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources. Commonly known as 400kV XLPE cable systems for HVDC applications.

Though we now know a little bit about high voltage cables, knowing the cable specification and type is far from enough to choose the right cable for your applications; it is the size of the cable that counts.
High voltage cable size chart.
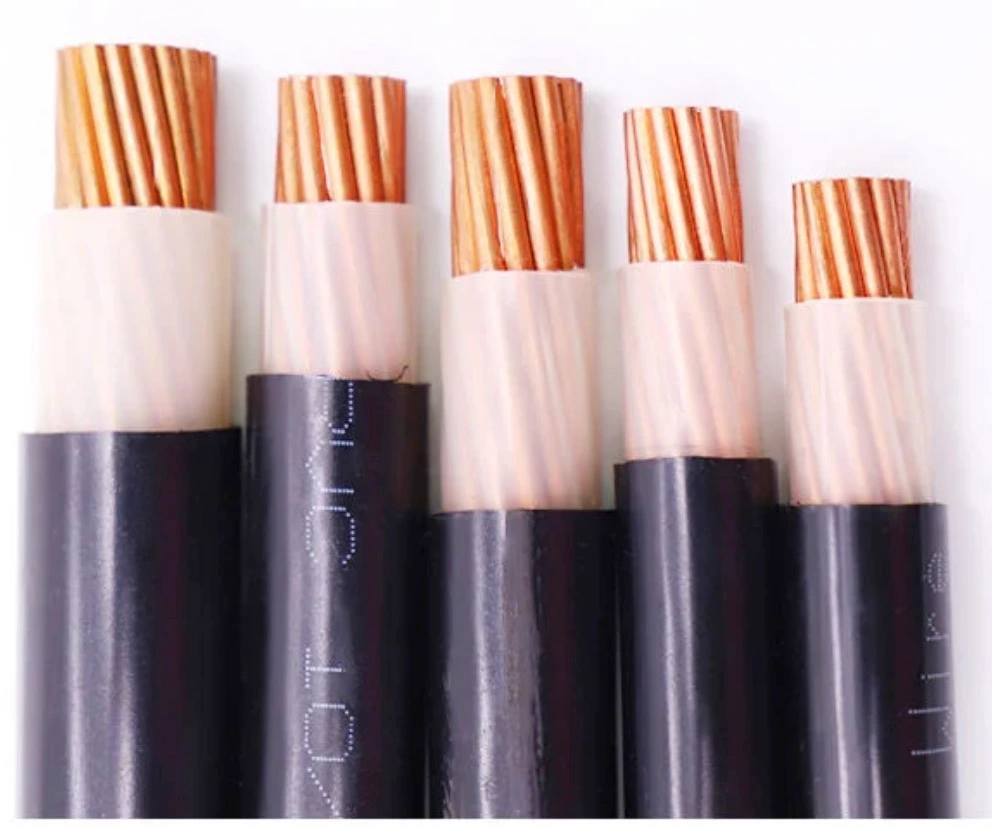
High voltage wire sizing is a crucial aspect in choosing the right HT cable since it’s hard to tell whether it’s large or small just from imagination, therefore, we are here to offer some basic size charts for your reference.
| High Voltage Cable Size Chart | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-sectional (mm²) | Conductor diameter (mm) | Insulated Thickness (mm) | AL Sheath Thickness (mm) | Sheath Thickness (mm) | Cable Diameter (mm) | Weight of the cable (KG/KM) |
| 400 | 23.8 | 27 | 2.4 | 5 | 116 | 14342 |
| 500 | 26.6 | 27 | 2.4 | 5 | 119 | 15629 |
| 630 | 30 | 26 | 2.4 | 5 | 121 | 16946 |
| 800 | 33.8 | 25 | 2.4 | 5 | 123 | 19069 |
| 1000 | 38.7 | 24 | 2.6 | 5 | 126 | 20970 |
| 1200 | 42.4 | 24 | 2.6 | 5 | 129 | 23270 |
| 1400 | 45.8 | 24 | 2.6 | 5 | 133 | 25525 |
| 1600 | 49 | 24 | 2.6 | 5 | 136 | 27774 |
| 1800 | 51.9 | 24 | 2.6 | 5 | 139 | 30112 |
| 2000 | 54.7 | 24 | 2.8 | 5 | 142 | 32383 |
| 2500 | 61.2 | 24 | 2.8 | 5 | 149 | 37780 |
With the table above, you will have a more visual understanding of hv cable sizes, helping to improve system efficiency and safety. And due to the potential hazard of high voltage cables being obvious to all, the benefits of learning to identify high voltage cabling are numerous, not only does it enrich your knowledge but could save your life in critical moments. Keep scrolling.
Learn More:How To Choose The Optimal Electrical Cable Size?
How to identify the high voltage cable?
Identifying high-voltage cables is a critical skill for anyone who works with electrical systems or encounters them in various settings to prevent accidents and promote safety. Here we offer some simple and obvious ways to recognize it:
Markings: Check the rated voltage markings in kilovolts on the cable insulation or jacket.
Safety signs and labels: In areas where high voltage cables are present, such as electrical substations, power distribution systems, or industrial facilities, fencing, restricted access safety signs, and warning signs are typically installed to indicate the presence of HV cables; warning signs typically use standard hv symbols, such as lightning bolts within a triangle or a zigzag line, and may include voltage ratings.
Color Coding: In many regions, high voltage electric cables are color-coded to distinguish them from lower-voltage cables. Though high voltage wire color can vary by country and region, they are generally bright orange or red.
Also Read:Understanding Electrical Cable Colours
Diameter and Size: High voltage cables are often more prominent in diameter compared to lower voltage cables. They may have thicker insulation and a larger conductor size to handle the higher voltage levels and associated electrical stress.
Breaking it down further, there are also ways to tell the accurate voltage from the AC or DC just by looking and counting:
Towers or poles: Towers generally set up high-voltage lines, for lines of 35 kV and above, with transformers and insulators on the towers and no trees nearby; poles mainly erect medium- and low-voltage lines, generally used for lines of 10 kV and below, which may have trees running through them.
AC or DC: DC towers have only positive and negative conductors; AC is three-phase with three or six conductors (six conductors on the same tower for the same tower double-back erection line).
It is worth noting that AC power is generally used in the conductor splitting method, which refers to the use of multiple harnesses fixed together instead of the original one whole conductor, the advantage is that it can inhibit corona discharge, optimize the line parameters, and improve the transmission capacity of the line and the stability of the power system operation.
AC transmission line splitting is as follows:
- Single split conductor voltage level is generally 110 kV, 35 kV, and below, some 220 kV lines will also use single split conductor.

- Two-split conductor voltage level of 220 kV or 330 kV.
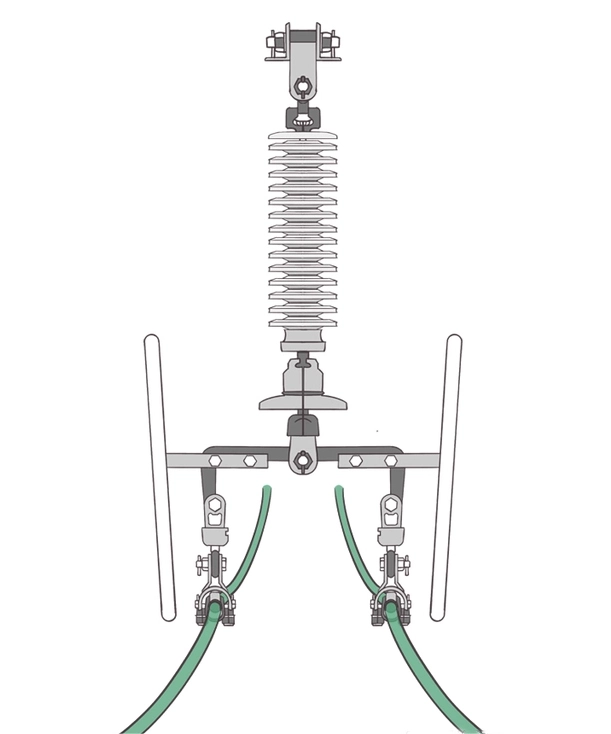
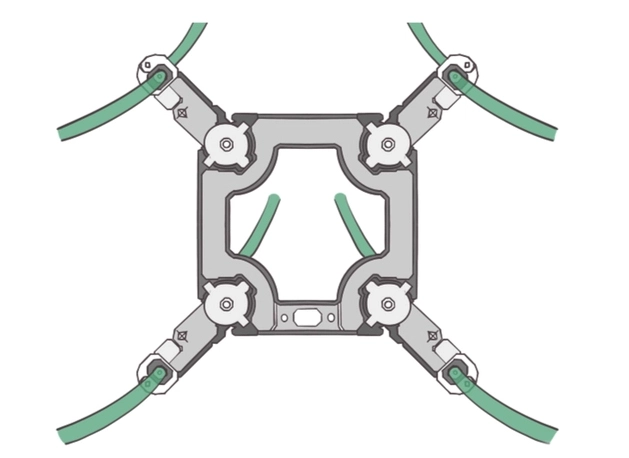
- Four split conductor voltage level is generally 500 kV.
After systematically studying the theoretical knowledge of high-voltage cables, the following is naturally the practical part of the operation.
How to connect high-voltage cables?
Connecting high-voltage cables is a potentially risky process and we have provided you with a step-by-step guide to minimize it:
Step2. Inspection: Carefully inspect high voltage cables for signs of damage, wear, or deterioration; damaged cables must be repaired or replaced before further use.
Step3. Cable Preparation: Strip off the sheath, metal layer, buffer layer, insulation, and warping tape in order to expose the conductors.
Step4. Connector Selection: Select the appropriate high voltage cable connectors for the particular cable type and application. The connector must match the rated voltage and current capacity of the cable.
Step5. Connector Assembly: a. Crimp cable lugs onto the stripped conductor ends with the appropriate crimping tool, ensuring a tight fit.
- Clean connector surfaces and cable lugs with a dry towel to remove dirt, grease, or oxides.
- Align the cable lugs with the connector on the equipment or terminal block.
- Secure the connector with the specified bolts and nuts and tighten it to the required torque value using a torque wrench.
Step6. Insulation and Sealing: Apply heat shrink tubing or insulating tape to cover the connection and protect exposed wires from moisture, contamination, and electrical discharge.
Step7. Connection Verification: Rigorous high voltage cable testing is required after connection to verify integrity and safety, which may include Hipot testing, insulation resistance tests, continuity tests, and other electrical tests.
Due to the inherent risks of working on high-voltage systems, feel free to consult a professional worker whenever you are not confident. And above steps can also be utilized on how to splice high voltage cable.
Bottom Line
All in all, high voltage cables serve as the backbone of our power infrastructure in an era driven by ever-increasing demands for electricity, and learning their specifications, types, sizes, identification, and connection is vital for our modern life, in which the ZW Cable is preferred high voltage cable manufacturer to meet the stringent demands of modern electrical systems, for they utilize the advanced technology and the strictest standards. For any need of high voltage wire, please do not hesitate to consult ZW; we will offer you the most preferential high voltage cable price list.