When we refer to the electrical cable size, we are really talking about the cable’s cross-section area; it’s usually measured in awg or mm². Cable size plays a vital role in electrical systems; the right size is half the battle of the project. Inappropriate size could not only affect the performance but even cause potential hazards.

The selection of cable sizes is indeed a worrying issue. Still, luckily you have found this article, which will only take you a few minutes but can solve your problems in identifying, choosing, and calculating wire size, with a wire gauge chart and specific uses for gauge wire size as your takeaway. Now let’s get to the topic.
How to identify electrical cable size?
Assuming you have a cable on hand and want to purchase based on it, how should you determine its size? The answer lies in the following steps:
Step 1. Check Cable Markings: Many cables have markings printed on the insulation or jacket. Look for units after the value, such as AWG (American Wire Gauge) or mm² (square millimeters), which indicate the cable size.

Step 2. Identify Color Codes: Sometimes, different sizes of cables, especially low-voltage cables, may use different colored jackets. For example, in standard NM cable used in residential wiring, 14 AWG is white, 12 AWG is yellow, and 10 AWG is orange.
Also Read: Understanding electrical cable colours
Step 3. Measure the Cable Diameter: If the above information can’t be found, we can measure the diameter of the cable using calipers or a straightedge and then apply it to πr² (round cables) or width*height (flat cables) to get the cross-sectional area.
- Strip part of the outer insulation with wire strippers before measuring the round cable, then align the vernier caliper vertically with the cable, sliding the vernier scale along the main scale until the caliper slightly touches the widest point across the conductor, i.e. the diameter. As for flat cable, you should measure the width and height.
- Once you have the cross-sectional area, you can compare it to standard wire gauge charts(we have provided below), or an electrical cable size calculator can be used to determine the cable’s size.
Step 4. Use Cable Gauge Tool: Cable gauge tools such as round wire gauges and sheet metal gauges can help to quickly size electrical cables by inserting the end of the cable into the appropriate groove until the cable fits snugly.
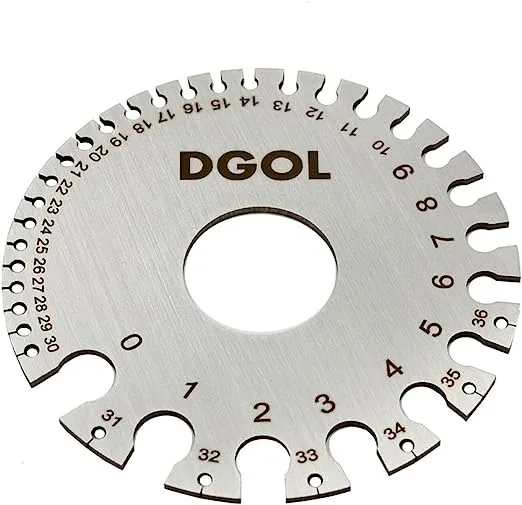

Learning how to measure cable size above will give us a general reference for the cable size on hand, and we will now discuss one of the most important concerns, that is, how to choose the required electric cable size correctly without a specimen. Keep scrolling.
What size electric cable do I need?
As the lifeline of our modern life, electrical cables have evolved into various types, from the widely used THHN and house wire for building wiring to the specialized armored cable for outdoor applications; each cable type comes with distinct features that make it suitable for certain environments and purposes. However, though electrical cable types address compatibility with different conditions, cable size is all about effectively handling current demands in hv, mv, or lv systems.
To determine the appropriate size of electrical wire you need, you must consider the following factors:
- Current Load: The maximum current the cable can carry, i.e. the sum of the electrical equipment or devices connected in the circuit, is the primary factor.
- Voltage: Standard residential systems typically operate at 120V or 240V, while industrial systems may operate at higher voltages.
- Voltage Drop: Ensure that the voltage drop of the selected cable is within the allowable range of the equipment. Voltage Drop (V) = Current (I) × Resistance (R).
- Cable Length: Determine the length of the cable run from the power source to the load. Longer cable runs can result in higher voltage drop, which may require a larger cable size.
- Cable Type: Choose the appropriate cable type for your application, such as THHN, control cable, armored cable, or specialty cable. Different cable types have different ampacity ratings and are suitable for different
- Ambient Temperature: Higher installation ambient temperature may require derating the cable’s ampacity.
- Safety Margin: Consider adding a safety margin of 20% to 25% to the calculated ampacity to account for occasional surges or future increases in electrical load.
- Installation Method: How the cable is installed can also impact its current-carrying capacity. For example, cables installed in conduits generally have higher ampacity than cables in free air.
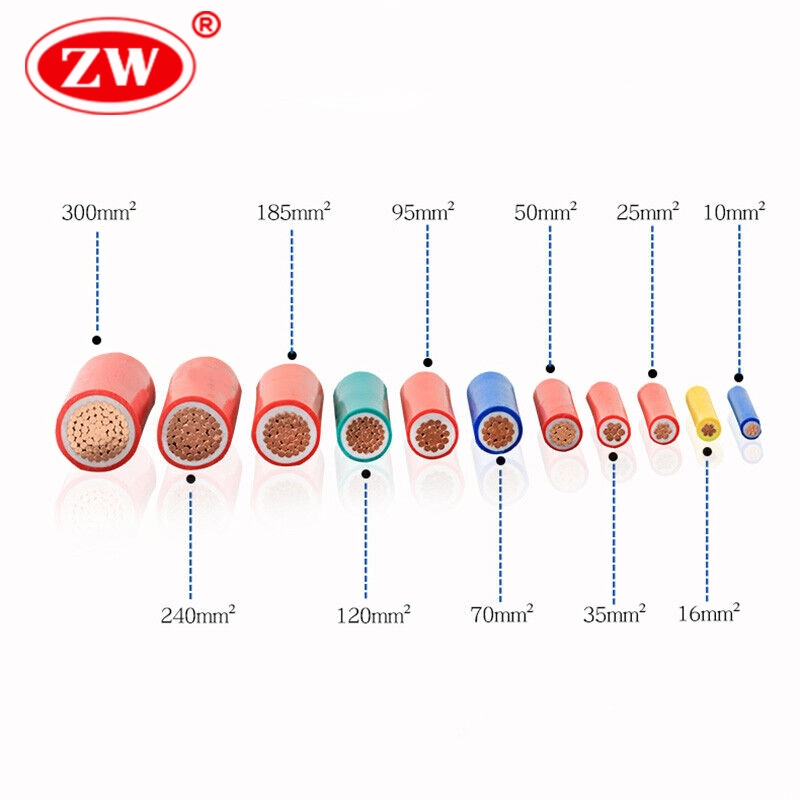
With due consideration of the above factors, you can easily select the correct wire gauge size. But just as the consumer asks, how can I accurately calculate the size of cable without advice when I already know all the data for my application? The answer is right below.
How to calculate electrical cable size.
Cable sizing directly affects the performance and overall reliability of the system, and the cable dimensions calculation is an integral process to ensure proper wire selection. To calculate the electrical wire size, you can use the following formula:
Cable Size (Cross-sectional Area) = (I * L * K) / (V * Φ)
Where:
I is the current load in amperes (A) that the cable need to carry.
L is the cable run length in feet (ft) or meters (m).
K is the resistivity of the cable material (for copper, K is typically 12.9 (metric units) or 21.2 (imperial units)).
V is the voltage drop in volts (V) allowed for the specific installation (Typically 3% to 5% for low voltage distribution and lighting systems ).
Φ is the power factor of the load (usually 0.8 for standard power factor loads).
Isn’t it easy to operate? If you want to save even more effort, we also provide a table of electrical cable sizes with their current ratings for your reference.
Electrical cable size chart.
Cables that are too small can lead to overheating and short circuits, while cables that are too large could be wasteful and cumbersome. To avoid these issues, we provide a cable chart where the respective current carrying capacity, insulation thickness, resistance, and weight of copper and aluminum conductors can be found:
| Electrical Cable Size Chart Amps | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-section Area (mm²) | Insulation Thickness (mm) | Copper Carrying Current in the Air at 25℃ (A) | Aluminum Carrying Current in the Air at 25℃ (A) | Copper Core Weight (kg/KM) | Aluminum Core Weight (kg/KM) | Resistance (Ohm/KM) |
| 1.5 | 0.8 | 24 | - | 58 | - | 13.5 |
| 2.5 | 0.8 | 32 | 25 | 71 | 56 | 8.45 |
| 4.0 | 1.0 | 45 | 34 | 97 | 73 | 5.31 |
| 6.0 | 1.0 | 56 | 43 | 121 | 84 | 3.36 |
| 10 | 1.0 | 80 | 61 | 177 | 111 | 2.11 |
| 16 | 1.0 | 106 | 83 | 239 | 139 | 1.33 |
| 25 | 1.2 | 143 | 111 | 349 | 190 | 0.84 |
| 35 | 1.2 | 175 | 133 | 451 | 232 | 0.62 |
| 50 | 1.4 | 223 | 170 | 624 | 309 | 0.41 |
| 70 | 1.4 | 265 | 207 | 821 | 384 | 0.36 |
| 95 | 1.6 | 329 | 254 | 1085 | 491 | 0.19 |
| 120 | 1.6 | 382 | 297 | 1338 | 589 | 0.15 |
| 150 | 1.8 | 445 | 339 | 1642 | 706 | 0.12 |
| 185 | 2.0 | 519 | 392 | 2032 | 858 | 0.099 |
| 240 | 2.2 | 609 | 472 | 2605 | 1091 | 0.075 |
| 300 | 2.4 | 700 | 541 | 3238 | 1340 | 0.061 |
For your convenience, we have converted awg to mm; you can select the corresponding size according to the application’s specific requirements,, such as current-carrying capacity, voltage drop, and so on.
Uses of Different Cable Sizes.
To deepen the concept of wire cable sizes, here is a table of cable size purposes, which is finely divided into specific devices that you can find in your daily life.
| Cable sizes and the purpose of each cable size | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cable Size (mm²) | AWG | Current Consumption | Used |
| 1.5 | 16 | Low | Sensors, alarm systems and doorbells. |
| 2.5 | 14 | Relatively Low | Outdoor lighting, hand mixer,and vacuum cleaner. |
| 4 | 12 | Medium | Refrigerator, dishwasher, and toaster oven. |
| 6 | 10 | Medium | Submersible pump, small welding machine and air compressor. |
| 10 | 8 | Medium-high | Electric water heater, heavy-duty drill, and industrial fan. |
| 16 | 6 | High | Large welding machine and industrial mixer. |
| 25 | 4 | Very high | Heavy equipment and industrial plant power distribution. |
Whether you’re wiring small appliances, lighting fixtures, or heavy industrial machinery, the table above can serve as a general guide to choosing the right wire size for you.
Bottle line.
Sizing electrical cable is an essential step in ensuring secure and efficient electrical installations. If you have learned to recognize, calculate, and choose wire size from this article, it will save you a lot of hassles and unnecessary expenses in your life. To further simplify this process, you can explore reliable brands like ZW Cable, which offers all kinds of sizes according to the electrical cable types list. ZW Cable’s commitment to excellence and reliability makes it a trusted choice.