Edison created direct current in the late 1880s, and it was used to power low-voltage household lights. Street lamps were powered by high-voltage AC electricity. Once George Westinghouse’s company discovered it, there was intense competition. He employed transformers to lower high AC voltages for domestic use.
In the end, AC won because it was more efficient than DC. It can transport power over long distances without experiencing any loss, making stepping down voltages considerably simpler.
The fundamentals of AC and DC help to navigate the world of electricity and their application in everyday life. This article will examine the difference between AC and DC currents and how they impact our daily lives.
Concept of AC
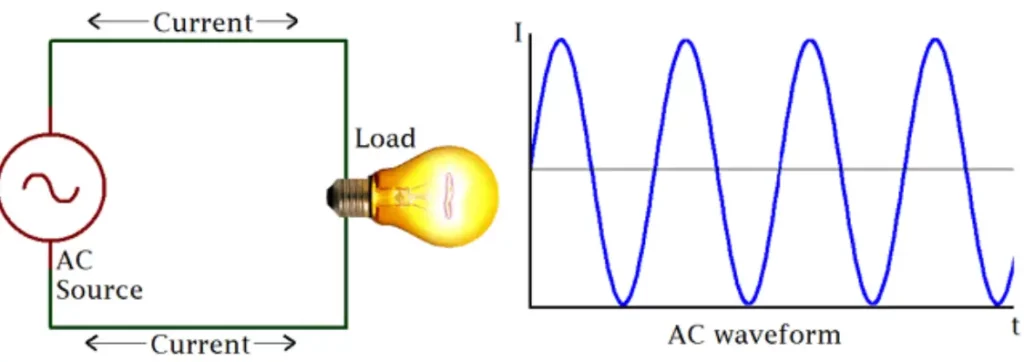
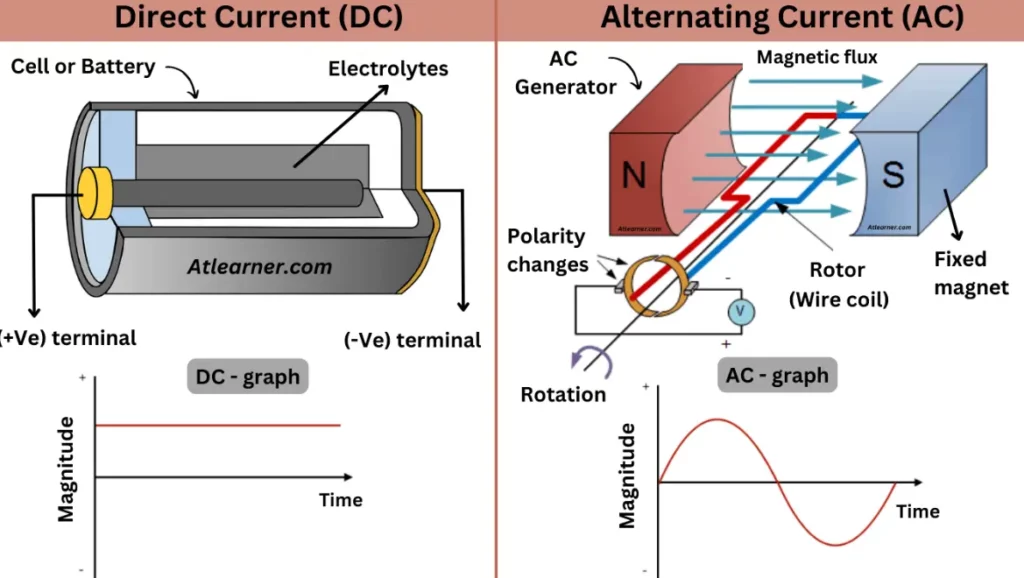
Alternating Current (AC), changes its polarity and magnitude periodically and continuously with respect to time. An alternator generates an alternating current that occurs when the electrical current periodically inverts its directions. Electrons cause the flow of AC current from positive to negative. The wave produced by AC is known as the sinusoidal AC wave.
Various Ways of Generating AC
- Alternators
It is one of the common methods of generating AC. It generated electrical energy by converting mechanical energy with the use of electromagnetic induction.
- Generators
Like alternators, the AC generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The major difference lies in the size and application type. Generators are often used to back up power and as portable energy sources.
- Inverters
If you want to generate AC current from DC then you need the inverter system. The DC from batteries, solar panels are converted using inverter into AC. It is useful for the renewable energy system too.
Advantages of AC:
Voltage conversion
The main benefit of AC is; it can be stepped up or down in voltage easily with transformers. It helps to transmit power efficiently for long-distance.
Easy conversion to end-use voltages
The majority of appliances and end-use devices need AC power. Thus, end-use power distribution can be simplified and made more effective through AC power grids.
Power-sharing capability
AC electricity can exchange power between sources and loads far more easily that makes the grid more flexible and stable.
Lower equipment costs
Due to its simplicity, AC equipment might be more affordable than DC equipment.
Disadvantages of AC in power grids:
Complex grid design
The inclination towards electromagnetic induction in AC circuits and grids makes their design complex. Compared to DC circuits, it may require advanced equipment and sensitive control systems.
Transmission losses
Long-distance AC power transmission can lead to increased energy losses because of transmission line resistance, especially at high voltages.
Frequency synchronization
There is a challenge in maintaining frequency synchronization with AC grid. AC power depends on the synchronization of its frequency with the grid, particularly when variable loads are present.
Reduced stability during transmission faults
Short circuits and voltage collapses are examples of transmission defects that can cause instability and blackouts in AC power systems. System-wide outages and cascading failures may result from it.
Applications of AC
Larger appliances such as freezers, air conditioners, dishwashers, washing machines, fans, and light bulbs require AC electricity. The HVAC system also uses AC power. The AC system is also applicable in industrial and factory environments where AC motors are used.
Concept of DC Power

The DC current is also known as Direct Current. It is a unidirectional flow of current. Both the magnitude and direction of the DC current are constant. The frequency of the DC current is zero due to constant direction and magnitude. In DC current, electrons move from high electron density to low electron density. Batteries, solar cells, fuel cells, etc are capable of producing direct current. DC is mostly used in electronics domain.
Various Ways to Generate DC
- Battery
The battery produces DC, through the chemical reaction inside the battery system. Some common types of batteries include lithium-ion, alkaline, and lead-acid. These batteries are suitable for various applications, ranging from small electronic devices to automation systems.
- Solar Cell
Photovoltaic cell helps to convert the solar light into DC electricity. These cells or panels are made from semiconductor materials which when expose to light generates the electric current.
- DC Generators
It converts mechanical energy into DC electricity. It is used in applications where constant DC power is required. For example, it is used in industrial systems or for charging batteries.
- Rectifiers
Rectifier helps to convert AC is converted into DC. This rectifier is a device that is composed of diodes that allows to flow current in one direction by converting AC into steady DC output.
Advantages of DC in power grids:
Suitable for renewable energy sources
Since renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines generate DC power, DC is a great fit for them.
Lower power losses
DC power transmission has smaller power losses than AC power transmission, resulting in greater efficiency.
Elimination of reactive power
DC power transmission does not need reactive power, which eliminates the need for power equipment like transformers and capacitors.
Efficient storage and retrieval
DC energy storage can be more efficient than AC energy storage due to the absence of conversion losses from AC to DC.
Voltage stability
Long-distance DC voltage transmission experiences reduced voltage drop. It increases power transmission and improves voltage stability.
Higher efficiency for charging EVs
Since DC power is used by electric vehicles, DC charging infrastructure can support the expanding electric vehicle market by offering faster and more efficient charger.
Disadvantages of DC in power grids
Limited distance
Due to the high voltage levels needed, DC power transmission is distance-limited and needs frequent converter stations.
High initial cost
DC power grid requires more advanced technology to built. Hence, the cost is more than for an AC power system.
Complex conversion process
For transmission, AC power must be converted to DC, adding complexity and expense.
Applications of DC Current
• Although DC electricity cannot be transmitted over great distances, it can be easily stored in the form of batteries.
• Radios, laptops, cell phones, and other electronic devices run on DC power.
• Electric and hybrid vehicles and automobiles use DC current.
Difference between AC and DC
| Alternating Current | Direct Current |
| It can easily transit to large distances and provide more power. | It can transit power for a the short distance. |
| It reverses its direction while flowing in a circuit. | It has uni-directional flow of the circuit. |
| It requires inductive as well as inductive loads. | It requires resistive loads. |
| Its magnitude depends upon varying time. | Its magnitude doesn’t depend upon varying time. It has constant magnitude. |
| It has a frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz depending upon the country. | It has zero frequency. |
| It can be converted to DC by using a rectifier. | It can be converted to AC by using an inverter. |
| It has a rotating magnet along the wire. | It has steady magnetism along the wire. |
| The wave is of AC in the form of Sinusoidal, Trapezoidal, Triangular, and Square. | It has pure and pulsating wave. |
| It is produced from A.C Generator and alternators. | It is produced from Cell or Battery. |
| Energy cannot be stored in a battery. | Energy cannot be stored in a battery. |
| Its power factor lies between 0 & 1. | Its power factor is always 1. |
| It is mainly used in industries, and homes. | It is used in electrical devices. |
Conversion from AC to DC Current
Rectification is the technique by which we can convert AC current to DC current. Rectifier converts AC into DC. Batteries can be used to store DC, but not AC. An inverter helps to convert DC to AC.
The Future of Electricity
Globally, there is a growing need for electricity, and in recent times, there has been an increase in demand for DC power lines. For instance, the use of electric vehicles (EVs), which need DC to run, is growing, and DC electricity is produced by renewable energy sources like solar and wind turbines. Significant advancements in battery technology have also made it possible to store large amounts of DC power.
HVDC technology is the transmission of electricity using DC as opposed to AC. This makes long-distance transmission effective and prevents large power loss due to electrical resistance. HVDC systems work by utilizing rectifiers to transform AC power into DC power. It transmits the DC power over a large distance, and then uses inverters to turn the DC electricity back into AC power to feed into nearby AC grids.
Multi-level converter modules (MMC), which enable smooth control of active and reactive power flow. MMCs enhance a level of versatility and controllability in HVDC systems.
MMCs modulate output voltage levels to increase stability, decrease harmonic distortion, and improve voltage regulation.
Conclusion
Thus, AC and DC are the two methods that the current flows. The flow of electrons through a conductor is known as current. The direction in which electrons flow determines the distinction between AC and DC. Electrons in DC move in a single direction with a constant magnitude. Electrons in AC moves forward and backward. The most effective method for sending power over long distances is through alternating current.
FAQs
Is a Battery AC or DC?
Yes, Battery is DC. Battery produces DC. Chemical processes within the battery provide DC voltage. Rather than storing electrical energy directly, a battery transforms electrical energy into chemical energy, which is then stored. This chemical energy is converted into electrical energy when the battery is operating. Rather than using AC electricity, the battery uses DC electrical energy.
What is the Difference between AC and DC Generators?
The electrical current in an AC generator reverses direction in a periodic way. Electrical current in a DC generator flows in one direction only.
How is AC cable different from Dc cable?
The DC cable has a simple design with positive and negative poles. However, the structure of AC cable is complex, it operates on a three-phase, four-wire system, and its cost is more than that of DC cable.
Why is DC not used at home?
DC current is not used in homes because DC is difficult to generate. Since batteries and photovoltaic cells produce direct current, it loses more power during transmission than alternating current. Also, the Peak current value of DC is less than AC.
Which is more powerful, AC or DC?
Higher voltages can be stored and transmitted by DC, whereas higher wattages can be carried and distributed by AC. So, in terms of wattage, AC is more powerful than DC. In terms of voltage, DC is more powerful than AC.
Is there a future of DC power?
In the future of electricity, both AC and DC electrical systems will be essential. DC is becoming more and more common in some applications, even though AC is still the most common method of power distribution and transmission.
Why is DC replaced by AC?
Unlike DC, AC can be transferred across large distances with little energy loss. When opposed to DC, there is less power loss during transmission in AC. AC has a higher peak current value than DC. The majority of our home’s appliances are inductively operated. If we utilize DC current for these appliances, they won’t function correctly. So, DC is replaced by AC.